Every 12 months the robots and satellites scientists have despatched to Mars make discoveries that assist us be taught extra in regards to the Red Planet’s previous and take us a step nearer to humanity’s potential future residing there — and this 12 months was no exception.
Despite the demise of NASA’s Ingenuity helicopter and a gaping gap in one of many Curiosity rover’s wheels, 2024 was nonetheless a banner 12 months for Martian discoveries, together with what occurred to the Red Planet’s magnetic subject and whether or not or not the alien world as soon as harbored extraterrestrial life.
From the long-lasting “spiders on Mars” and a large dog-shaped blob to an underground ocean and different newly found water deposits, listed below are our 10 favourite issues discovered on Mars this 12 months.
Related: 32 issues on Mars that appear to be they should not be there
Giant underground ocean
Arguably probably the most important improvement on Mars this 12 months was the revelation {that a} huge reservoir, containing sufficient water to cowl the Red Planet with a 1-mile-deep (1.6 kilometers) ocean, is lurking beneath the Martian floor.
NASA’s InSight lander found the underground reservoir in a layer of rock 7 to 13 miles (12 to twenty km) beneath the planet’s floor by analyzing greater than 4 years of “Marsquake” knowledge. Although no current drilling strategies can attain these depths on Earth, this reservoir might be vastly essential to future astronauts if we will discover a approach to attain it.
Researchers additionally famous that the buried ocean might harbor extraterrestrial life.
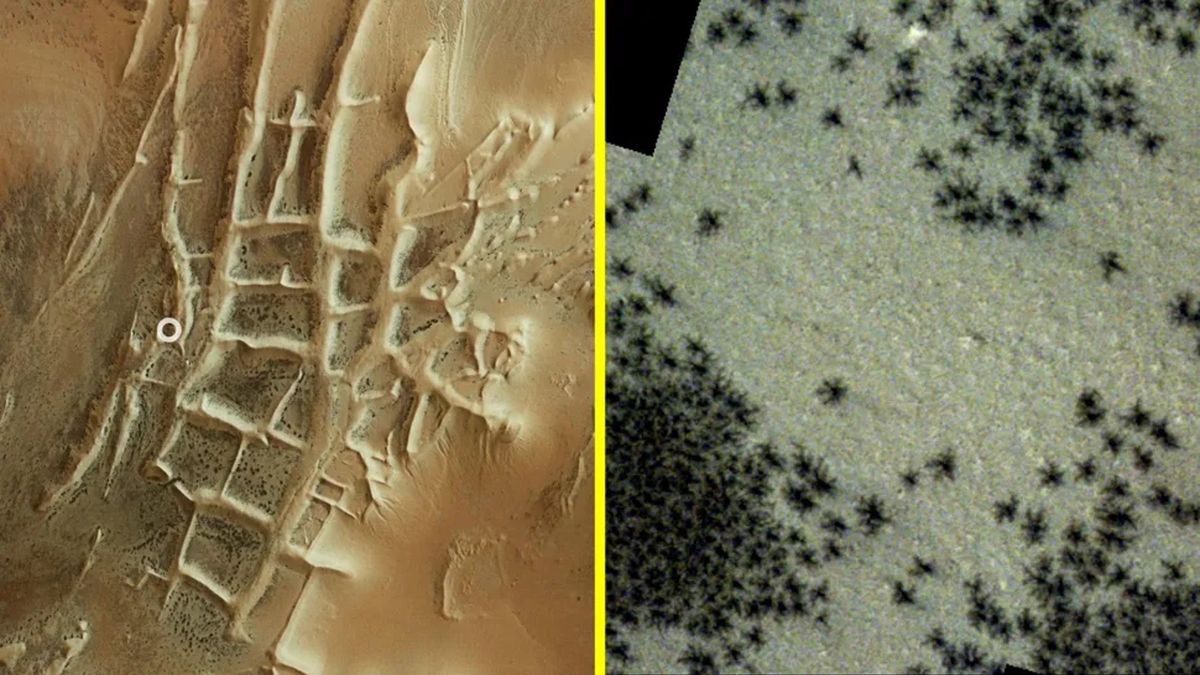
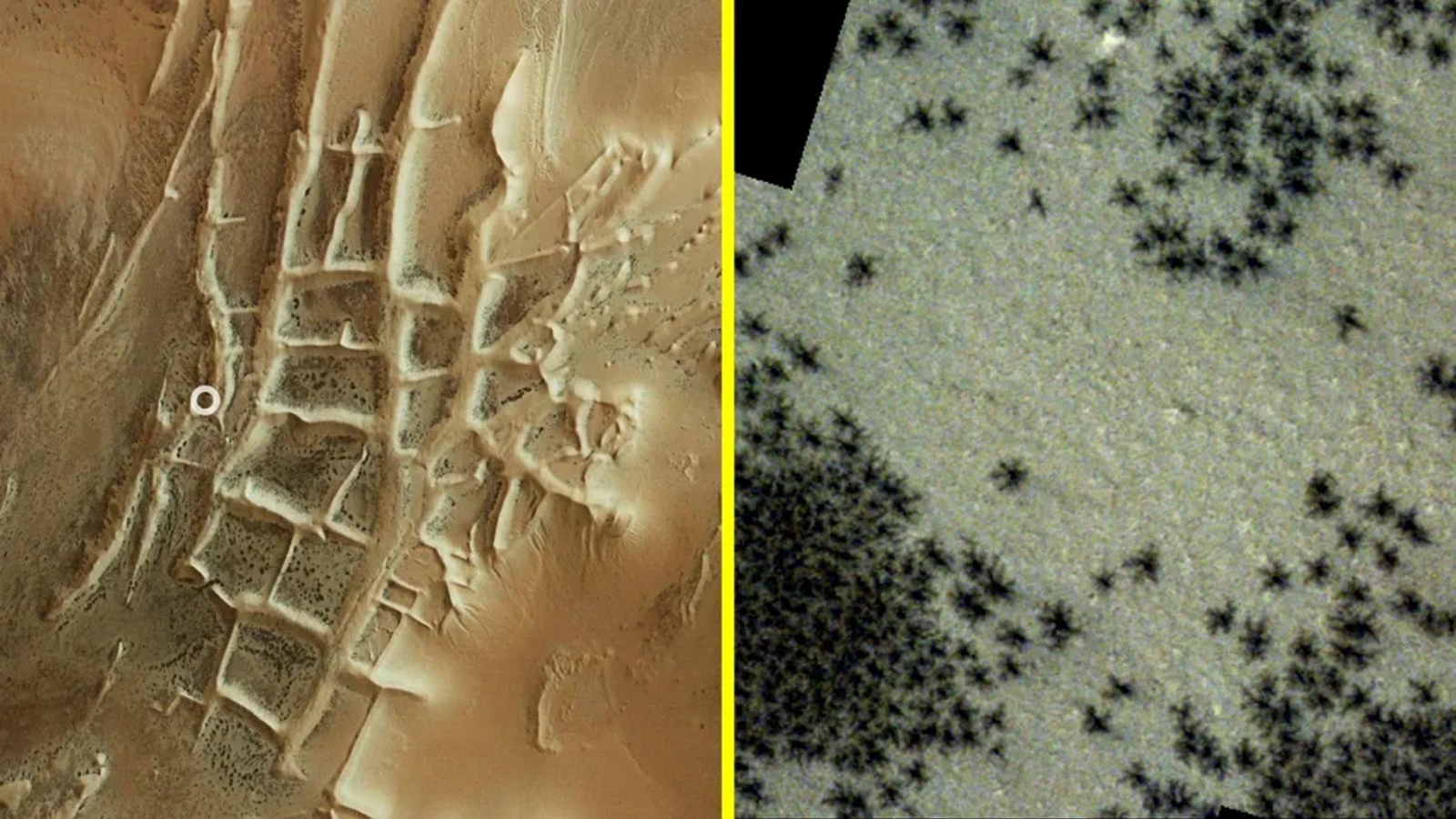
“Spiders” swarm “Inca City”
Spiders on Mars is the title given to spindly crack-like options that seem on the Red Planet’s floor through the Martian springtime when carbon dioxide ice sublimates — or turns immediately right into a gasoline — and drags up mud from under that settles into unusual shapes on the bottom.
Scientists have identified about these arachnid lookalikes for many years. But in April, images from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Mars Express orbiter and ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter revealed that the spiders had emerged in nice numbers at a area close to Mars’ south pole, often called the “Inca City” formation.
In September, researchers additionally created these spiders on Earth for the primary time, which is able to assist scientists be taught extra about these unusual buildings sooner or later.
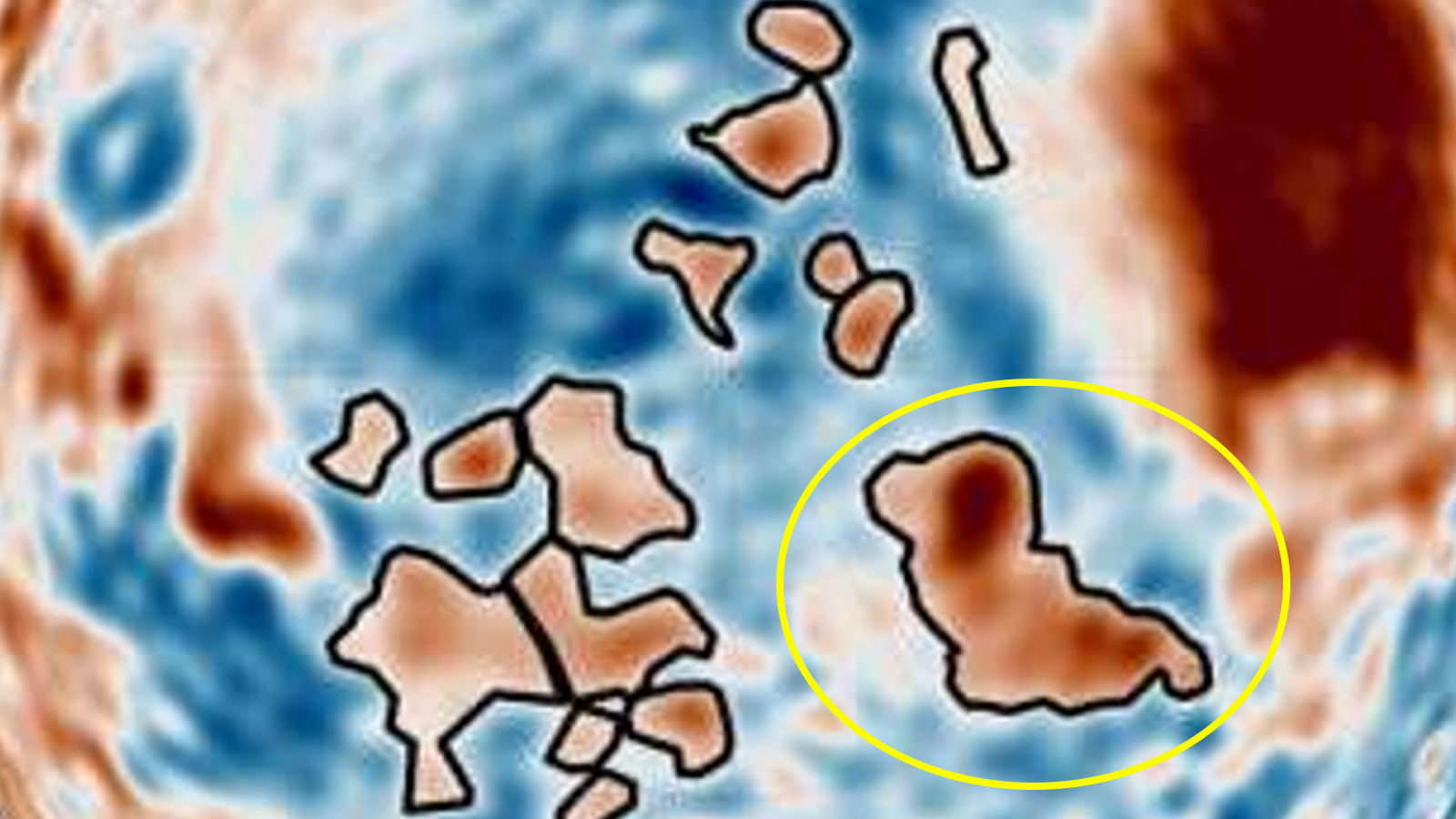
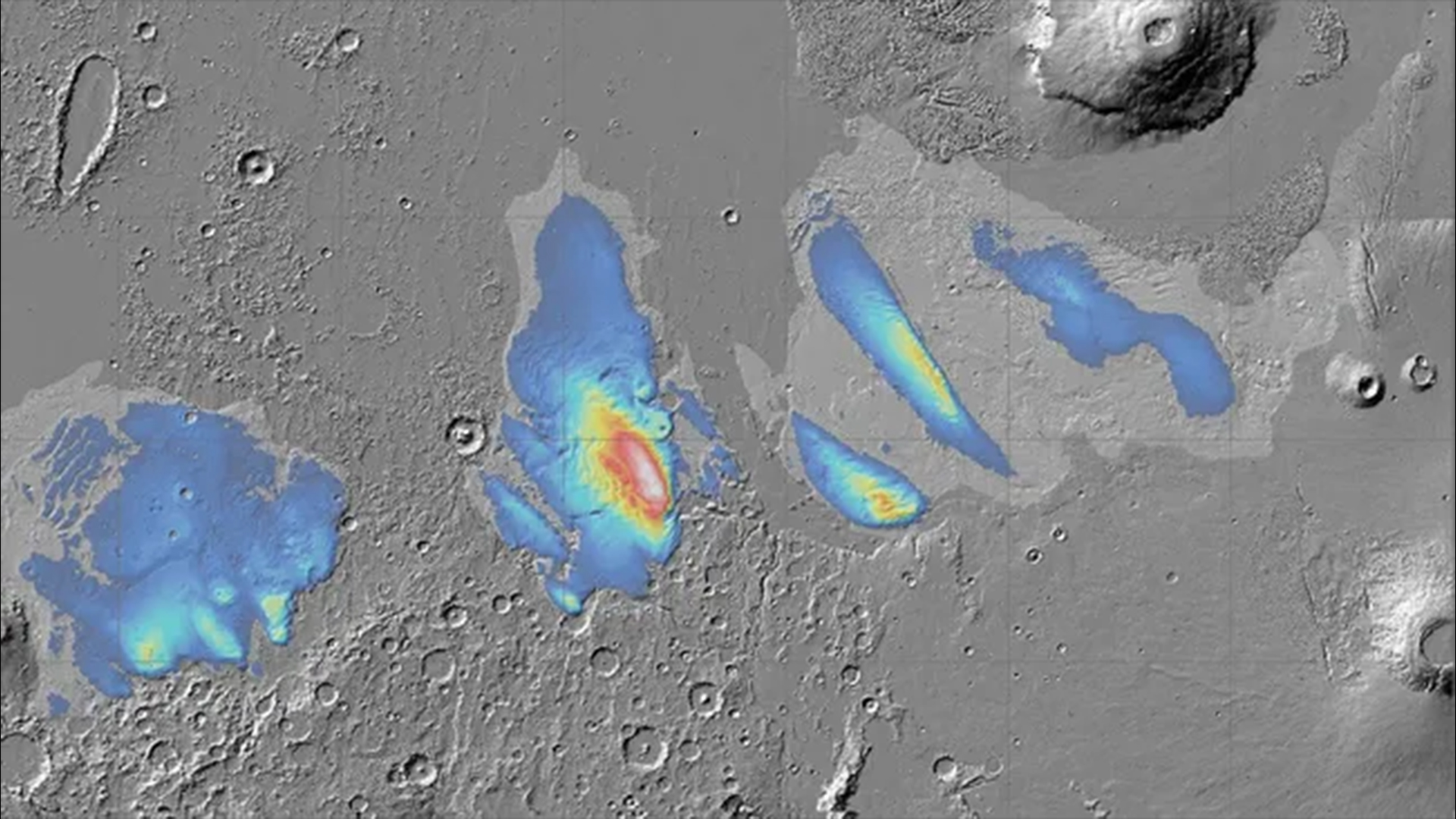
Martian canine and thriller blobs
In September, dozens of mysteriously dense blobs — together with a construction with a surprisingly canine form — had been discovered lurking beneath an historic seabed surrounding Mars’ north pole, due to a first-of-its-kind “gravity map.”
The new map was created utilizing knowledge from the InSight lander and Mars Express orbiter, revealing 20 underground buildings with densities between 19 to 25 kilos per cubic foot (300 and 400 kilograms per cubic meter) larger than the encircling bedrock. However, it’s presently unclear how they shaped and what they’re made from.
The similar analysis additionally confirmed the presence of a huge, solidified lava plume spanning 1,100 miles (1,750 km) beneath the photo voltaic system’s tallest peak, Olympus Mons — a large volcano standing greater than 16 miles (25 km) above Mars’ equator.
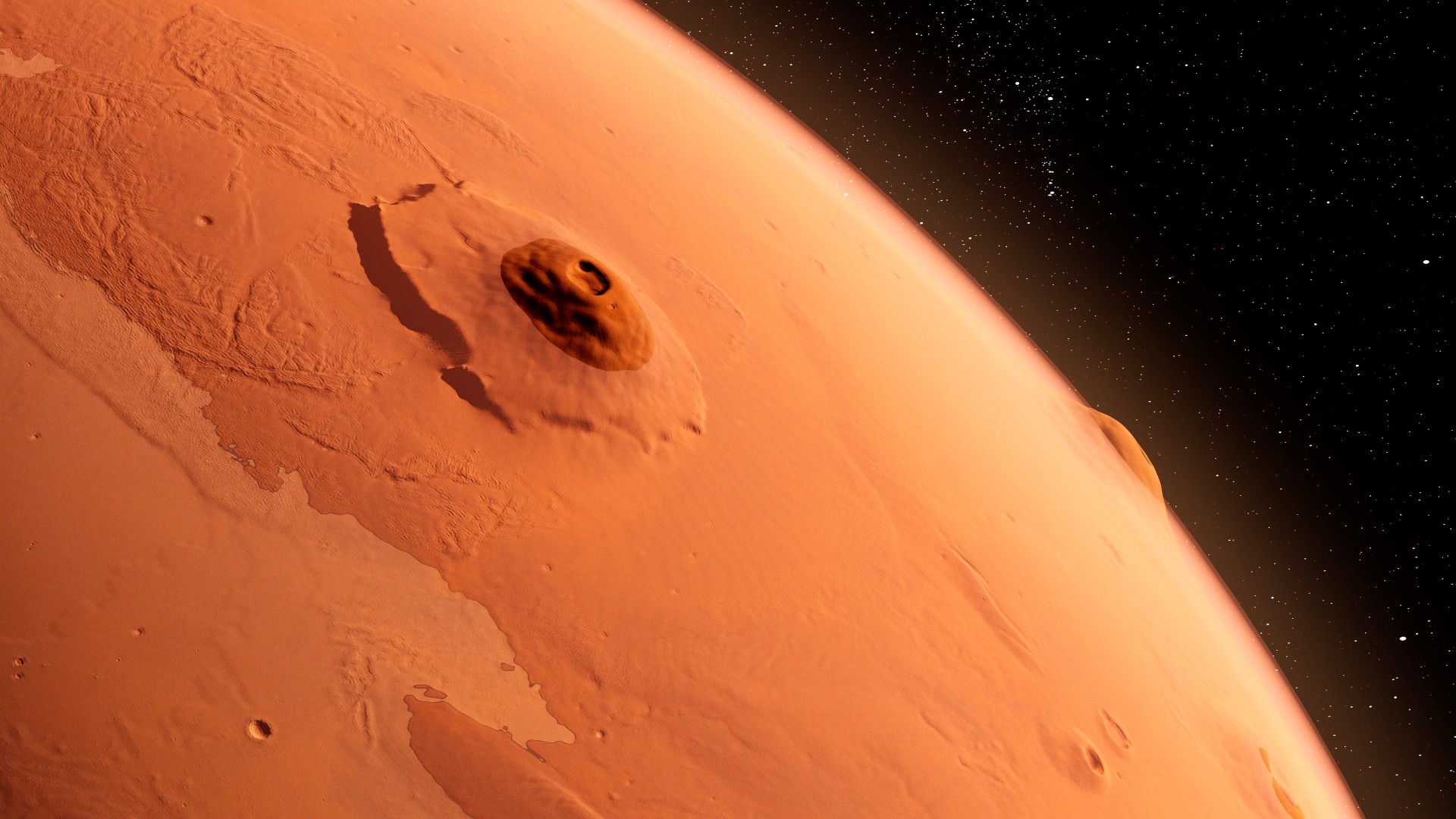
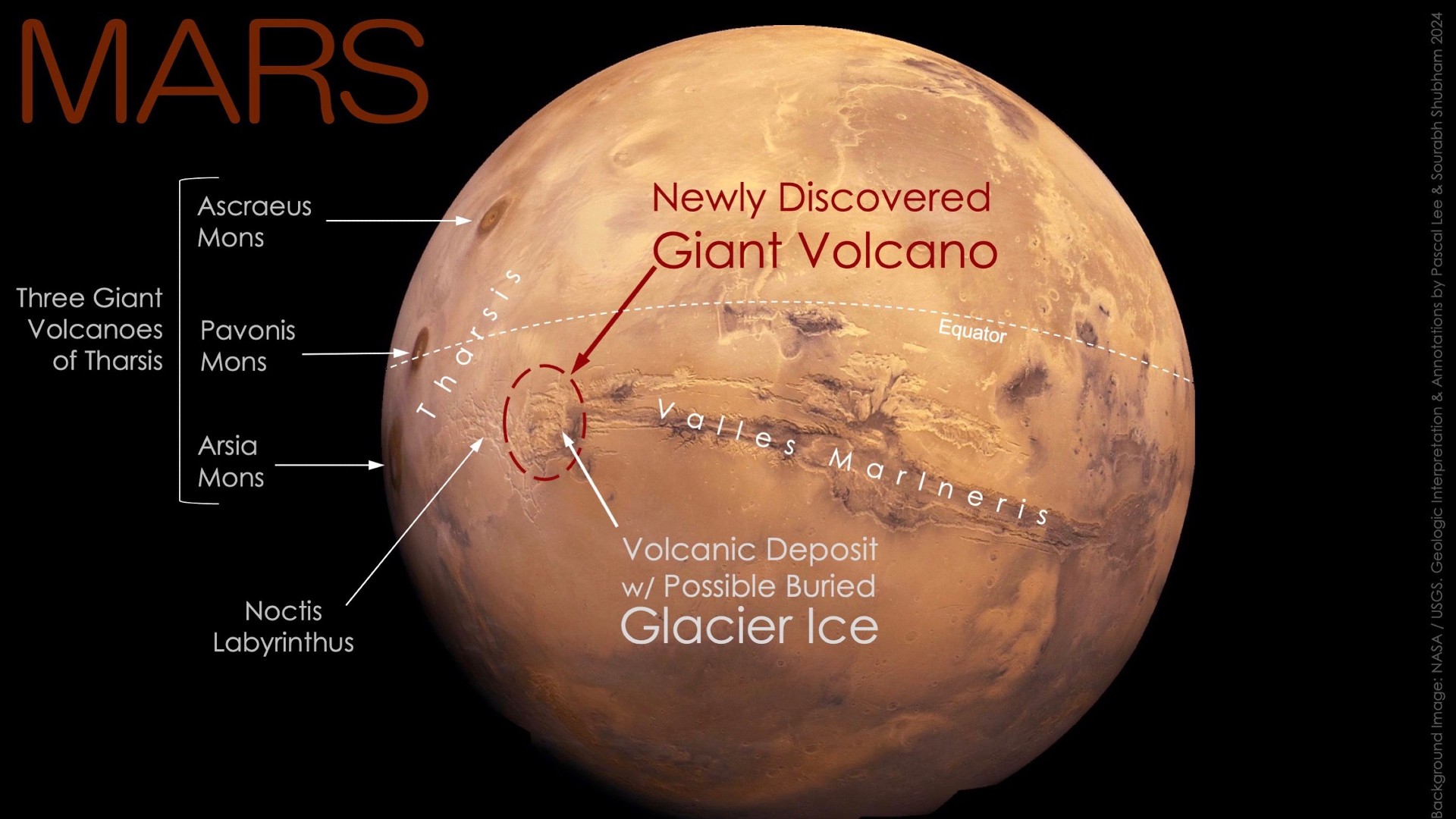
Massive volcano “hiding in plain sight”
Until lately, scientists assumed that we had already uncovered all of Mars’ largest buildings. But in March, scientists introduced the shock discovery of an infinite, long-dead volcano, spanning greater than 280 miles (450 km) throughout.
The big volcano, which continues to be unnamed, had gone unnoticed till now as a result of it has been massively eroded, that means little of it stays above floor. However, researchers learning the area seen the world was surrounded by the stays of historic slopes that might have as soon as towered above the encircling panorama.
Researchers additionally noticed what seems to be the stays of a sheet of buried glacier ice close to the bottom of the volcano, which might make the volcano a “prime location” for astrobiological analysis.
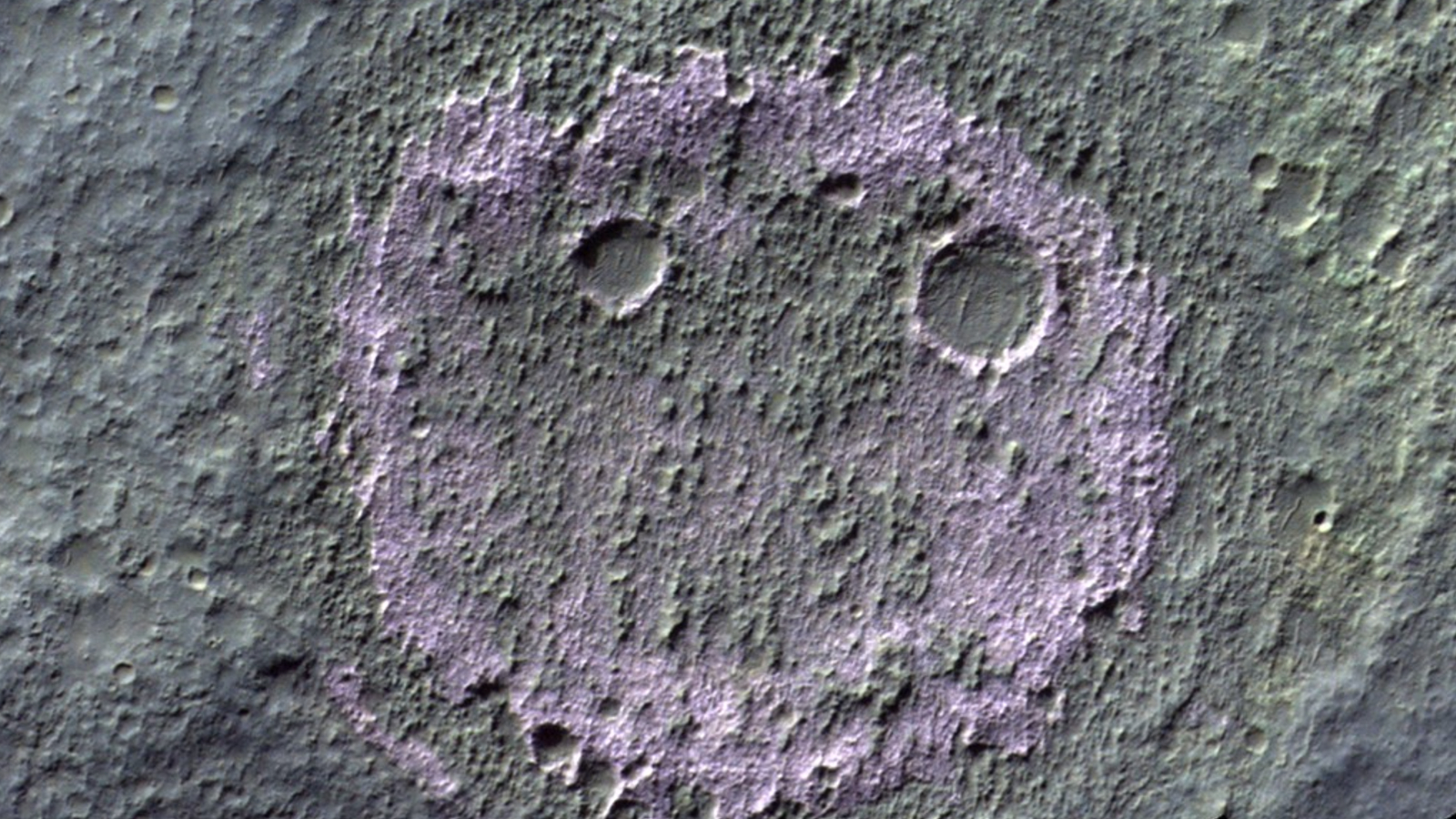
A salty smile
In September, researchers noticed a stunning “smiley face” beaming up from the floor of Mars as they surveyed the alien panorama.
The grinning form, which is made up of a hoop of historic chloride salt deposits with a pair of meteor-crater eyes, was snapped by ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter. The chloride salt seems pink within the picture as a result of it was snapped in infrared. Normally, the smile could be invisible to the bare eye.
The picture was taken as a part of a examine that surveyed nearly 1,000 related deposits, that are all thought to “present optimum circumstances for organic exercise and preservation,” researchers wrote.
Frosty peaks stuffed with water
To the bare eye, Martian volcanoes look as dry and barren as the remainder of the Red Planet. However, in June, researchers revealed that the lofty peaks of those dormant mountains are lined in water — within the type of frost.
In whole, researchers imagine there might be a minimum of 150,000 tons of water frost — the equal of 60 Olympic swimming swimming pools — on the 4 largest Martian peaks at any given time, photos captured by ESA’s Trace Gas Orbiter revealed.
Researchers had beforehand assumed this could be not possible as a result of the daylight on the equator, the place all of the volcanoes are situated, is robust sufficient to show any ice immediately into gasoline. However, the brand new examine reveals that whereas the frost sublimates away daily, it reforms in a single day.
Weird rocks
Mars’ floor is suffering from free rocks, and this 12 months NASA’s rovers discovered a bunch of bizarre ones.
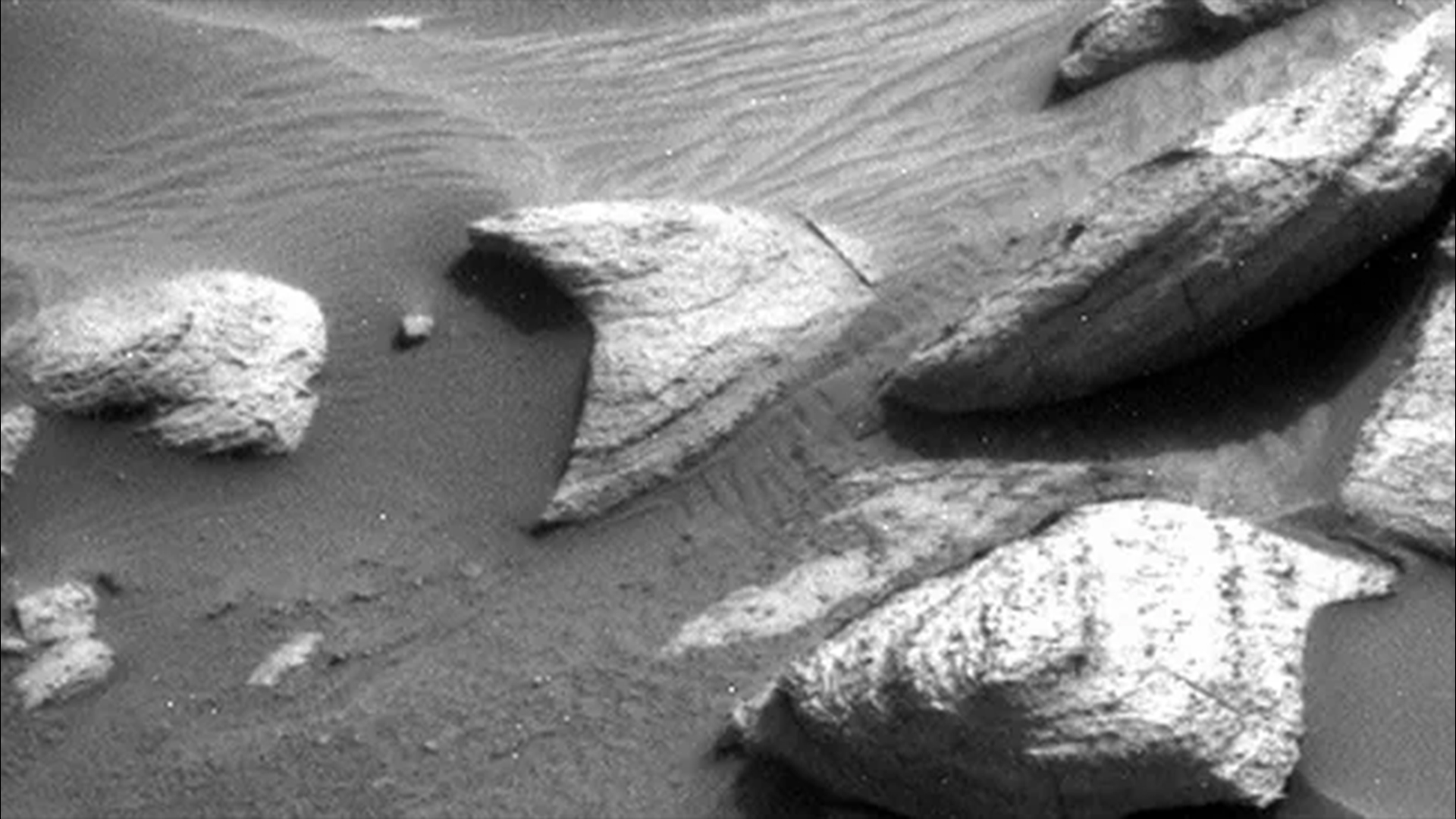
In January, the Curiosity rover noticed an arrowhead-shaped rock on the slopes of Mount Sharp that drew comparisons to the Starfleet badge from “Star Trek.”
In June, the Perseverance rover found a first-of-its-kind evenly coloured boulder within the Jezero Crater. Researchers stated the pale rock, dubbed “Atoko Point” after a equally unusual rock within the Grand Canyon, is in a “league of its personal” and will shed new gentle on Mars’ previous.
And in September, Perseverance additionally discovered an odd black-and-white striped “zebra rock” that’s not like the rest seen on the Red Planet. The precise origin of this rock, dubbed “Freya Castle,” is unknown, however researchers suspect it was made by way of volcanic processes.
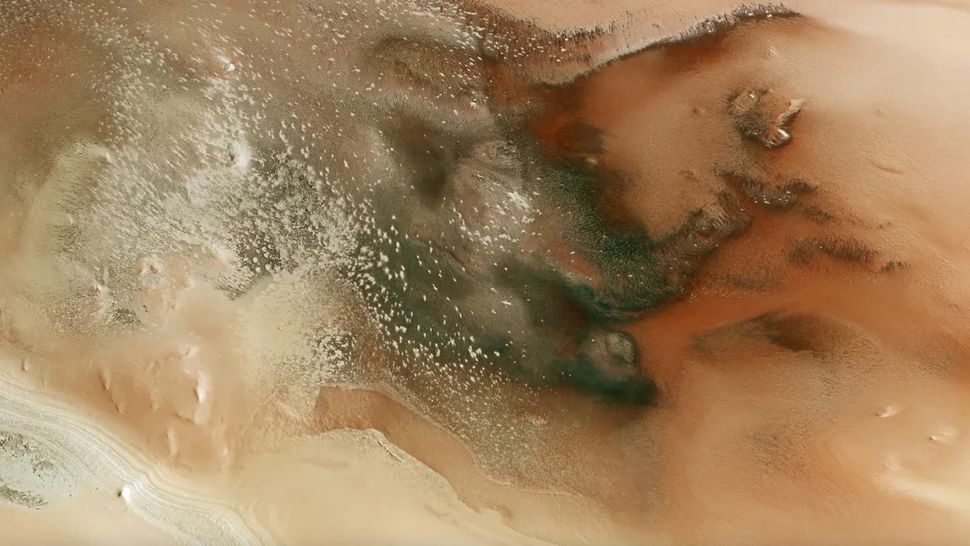
“Cryptic terrain” and darkish mud
In April, ESA’s Mars Orbiter captured photos of floor options across the planet’s south pole that researchers stated had been “surprisingly darkish in contrast with their icy environment.”
The scientists dubbed these areas “cryptic terrain” and imagine they’re attributable to patches of CO2 ice that repeatedly freeze and sublimate all year long. This is a seasonal cycle, the place the ice seems through the Martian autumn and disappears in spring.
The crew additionally recognized particular locations the place they imagine that darkish mud will get pulled up from the floor by the ice, just like how “spiders on Mars” kind, creating polygonal shapes the place the mud absorbs further daylight and causes ice to sublimate quicker.
Green spots
Thanks to early science fiction, most individuals’s psychological image of potential Martians in all probability resembles little inexperienced males. But whereas these stereotypical aliens have remained elusive thus far, the Perseverance rover did uncover little inexperienced spots on the Red Planet this 12 months.
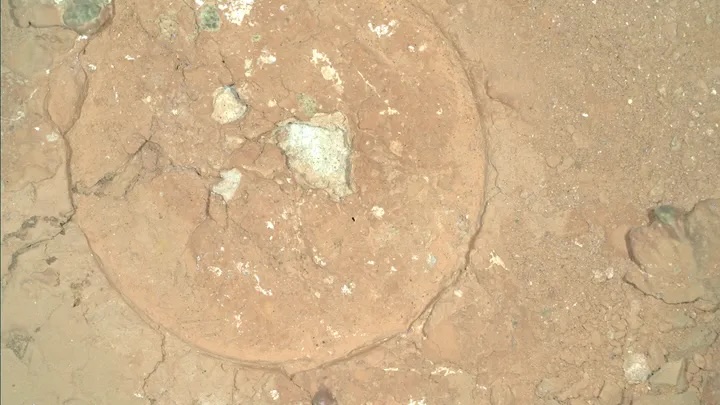
The tiny spots, which measure round 0.08 inches (0.2 centimeters) throughout, had been photographed by the rover in August because it surveyed an space dubbed “Serpentine Rapids.” The colourful patches had been embedded inside rocks alongside white dots. Green spots like these will be present in rocks on Earth when iron will get oxidized, giving the rocks an identical composition to rust — and researchers imagine the identical factor might be taking place on Mars.
On Earth, microbes usually assist oxidize rocks, hinting that the identical might have occurred on the Red Planet. However, the spots can even kind by way of abiotic components.
Buried ice chunks
In addition to the newly revealed underground ocean and the ample frost found on high of Mars’ volcanoes, researchers additionally found huge chunks of ice buried beneath the Red Planet’s equator this 12 months.
The submerged blocks, which lengthen 2.3 miles (3.7 km) under the floor, had been noticed utilizing radar photos captured by ESA’s Mars Express Orbiter. They are hiding beneath a geological formation known as the “Medusae Fossae Formation” and are lined by thick layers of ash and dirt.
It is unclear how the ice bought buried, however this isn’t the primary time that frozen water has been discovered beneath Mars’ equator, suggesting it might be a good suggestion to arrange future Martian bases close to the planet’s center.