Mosquitoes are usually related to spreading malaria relatively than stopping it, however in a brand new examine scientists have used the bugs to manage a promising new vaccine that would supply significantly better safety in opposition to the illness than present choices.
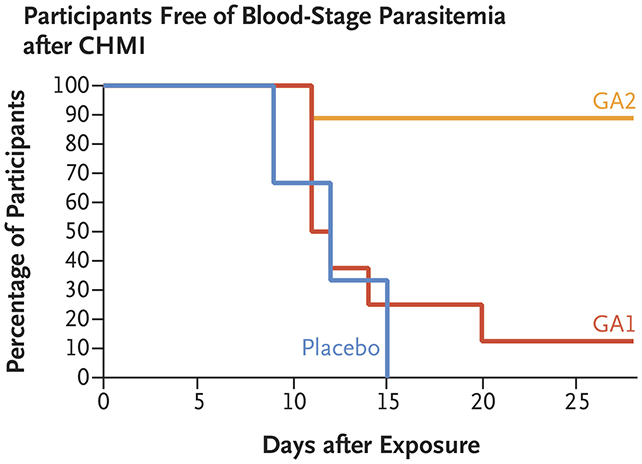
It’s the second technology of this explicit vaccine sort, and the development proven on this examine is important: eight out of 9 younger adults given the brand new vaccine have been protected in opposition to malaria, in contrast with one out of eight given the prevailing one.
The new vaccine, developed by researchers from Leiden University and Radboud University within the Netherlands, makes use of a genetically weakened model of the Plasmodium falciparum parasite that causes malaria in people. This model (GA2) would not set off malaria, however does put together the physique to protect in opposition to it.
“These crippled parasites are administered by way of a mosquito chunk and attain the human liver as common,” says vaccinologist Meta Roestenberg, from Leiden University. “But due to the gene turned off, this parasite can not full its growth within the liver, can not enter the bloodstream, and thus can not trigger illness signs.”
“Meanwhile, this crippled an infection does create a robust immune response within the liver, which may shield the particular person from an actual malaria an infection sooner or later.”
Having the parasite take longer to develop within the physique appears to assist: with GA2, P. falciparum takes virtually per week to mature contained in the liver, in contrast with 24 hours for GA1, the earlier model. That offers the immune system extra time to acknowledge what it’s, and work on combating again.
The GA2 vaccine triggered a much bigger and extra numerous set of immune cells, the examine confirmed, which can assist clarify its a lot improved effectiveness. Understanding why it really works so nicely will give researchers a greater concept of the right way to additional refine it.
Observed unwanted side effects have been comparatively minor, the researchers report, and principally concerned redness and itchiness across the mosquito bites. All individuals have been placed on a course of anti-malaria medicine after the examine information had been collected.
Progress continues to be made in tackling malaria, whether or not it is cutting it off on the supply or protecting the human body. However, we’re nonetheless seeing almost 250 million cases per year, and tons of of hundreds of deaths – and present vaccines only protect round 50-77 % of the inhabitants, typically for not for much longer than a yr.
As for the mosquito chunk supply system, this is not particularly unusual for analysis like this: it is helpful as a result of it means the the modified parasite is delivered and focused in the identical approach because the full-strength model, however it isn’t practical to make use of the method to really roll out a vaccine to the general public.
“In brief, the take a look at with our new crippled GA2 parasite performs very nicely,” says scientific microbiologist Matthew McCall, from Radboud University.
“We now plan to check vaccination with related GA2 parasites in actual life.”
The analysis has been revealed within the New England Journal of Medicine.




