A residing time capsule frozen within the depths of Lake Enigma in Antarctica comprises a novel ecosystem that has been remoted from the remainder of the world since its floor completely froze.
Now, scientists have retrieved samples of the distinctive microbes, which have survived in a large chamber of liquid contemporary water under greater than 9 meters (30 toes) of stable ice.
This ecosystem has probably existed inside the ice blister for 14 million years, which can have been when the lake first froze over on the finish of a a lot hotter interval of Earth.
Lake Enigma was regarded as frozen proper via, because it’s in Antarctica’s Northern Foothills, nestled between Amorphous and Boulder Clay glaciers, a area with a mean temperature of -14 °C (6.8 °F).
Led by microbiologists Francesco Smedile and Violetta la Cono from the Italian Institute of Polar Sciences, and geophysicist Stefano Urbini from Italy’s National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, the analysis crew used ground-penetrating radar to probe the lake’s composition, detecting the hid liquid bubble and drilling for samples of the water inside.
Special care was taken to stop contamination of this sheltered biome: an electrical drill was used for the primary 3 meters of ice, whereas the remaining layers had been uninterested in thermal head soften and sizzling water drilling. These use sterilized and heated water fashioned from ice crumbs collected in the course of the mechanical drilling section as a sort of liquid drill bit.

“Lake Enigma helps a phylogenetically numerous and high-biomass microbial ecosystem that stands distinctive amongst Antarctic perennially ice-covered lakes,” the crew writes.
“The ice-sealed planktonic and benthic microbiota of Lake Enigma doubtless signify persistent legacy biota that arose from the lake’s historical microbial ecosystem earlier than the freeze-up.”
These varied creatures, they found, occupy totally different roles inside a easy aquatic meals internet, starting from main manufacturing through photosynthesis, to ectosymbiosis and predation.
Among them had been forms of Pseudomonadota, Actinobacteriota, and Bacteroidota, together with an sudden abundance of Patescibacteria thriving within the subterranean water column.
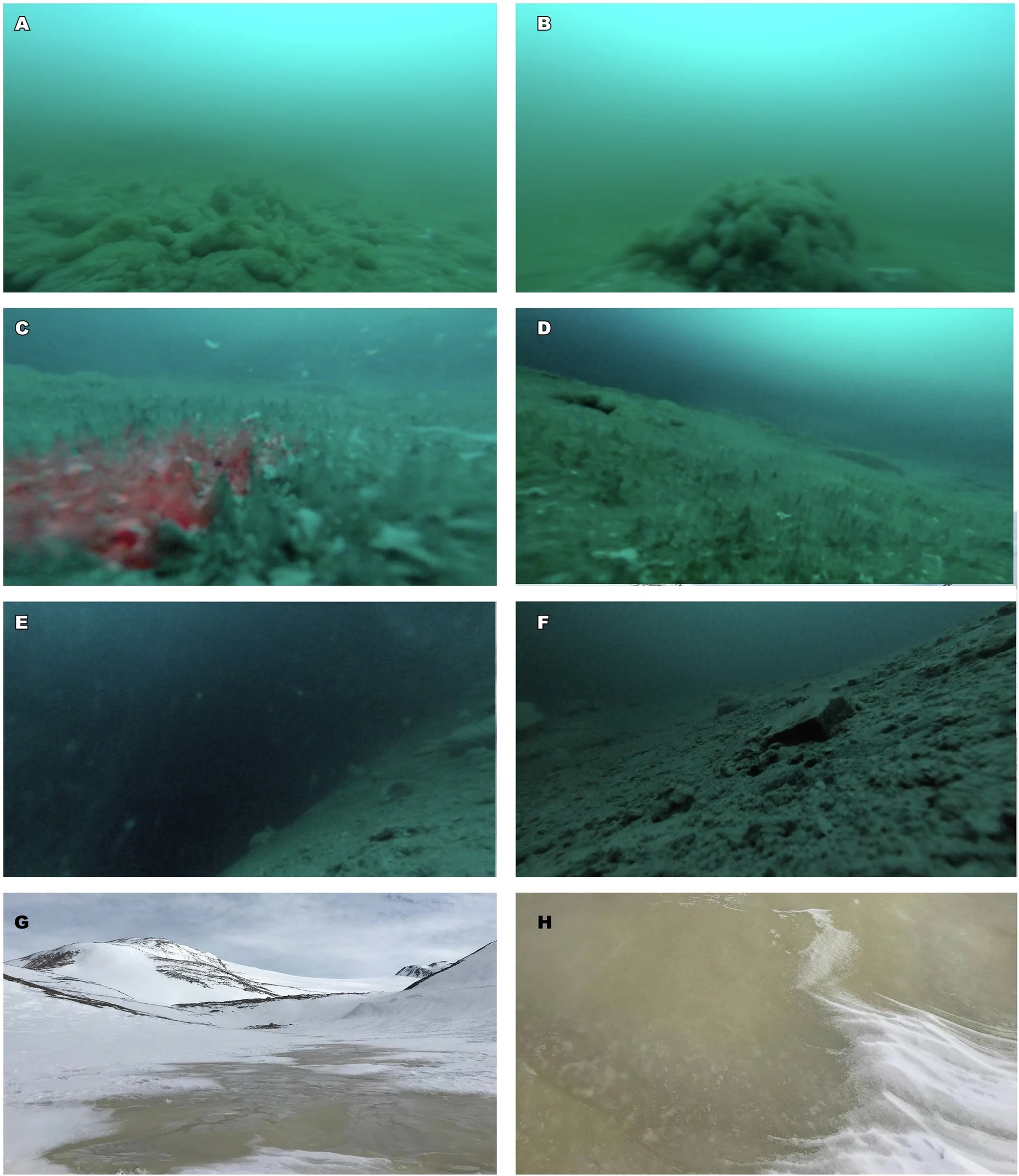
The lake ground, a tiny digital camera revealed, is roofed in biodiverse microbial mats, dominated by oxygen-producing cyanobacteria that had been in any other case absent from the lake’s ice and water column.
Some of those mats resembled a “crumpled thick carpet”, with the occasional protrusion of “massive amorphous tree-like buildings” that towered 40 centimeters excessive and spanned as much as 60 centimeters (2 toes) in diameter. Another drill location revealed the bacterial goop had fashioned a panorama of dune-like pinnacles.
The scientists suppose the extremely secure, pressurized, and chemically stratified water column, which is a minimum of 12 meters deep, might be ‘fed’ by the Amorphous Glacier close by.
The discovery of members of the Patescibacteria superphylum is particularly attention-grabbing as a result of, though they’ve been present in different low-oxygen environments in Antarctica, they’ve by no means been seen in an ice-covered lake earlier than.
The water column of Lake Enigma has abnormally excessive ranges of dissolved oxygen – not the standard habitat for Patescibacteria.
This superphylum is assumed to make up a large portion of the microbial range on Earth, and but evades detection in tradition and PCR assays, incomes it the nickname of ‘microbial darkish matter’.
These micro organism are extraordinarily small and very simple, missing most of the traditional capabilities of different microbes. As a outcome, they’re virtually all the time symbiotic with one other micro organism or archaea host.
“The ultrasmall Patescibacteria particularly might play uncommon roles within the lake’s ecosystem that don’t play out in different ice-covered Antarctic lakes,” the authors word.
This analysis was printed in Communications Earth & Environment.