The international reliance on fossil fuels, notably in transportation, has extreme penalties for the setting and public well being. Fossil fuels are a number one supply of greenhouse fuel emissions, driving local weather change and impacting respiratory well being.
A groundbreaking improvement from Wuhan University, nevertheless, hints at a future the place jet propulsion relies upon totally on electrical energy and air.
The Fossil Fuel Challenge
Transportation is significant for contemporary life, however its dependence on fossil fuels comes at a big environmental value. The combustion of those fuels powers autos, planes, and industrial gear whereas contributing practically 29% of greenhouse fuel emissions, in keeping with the Environmental Protection Agency. The pressing want for sustainable options has spurred innovation.
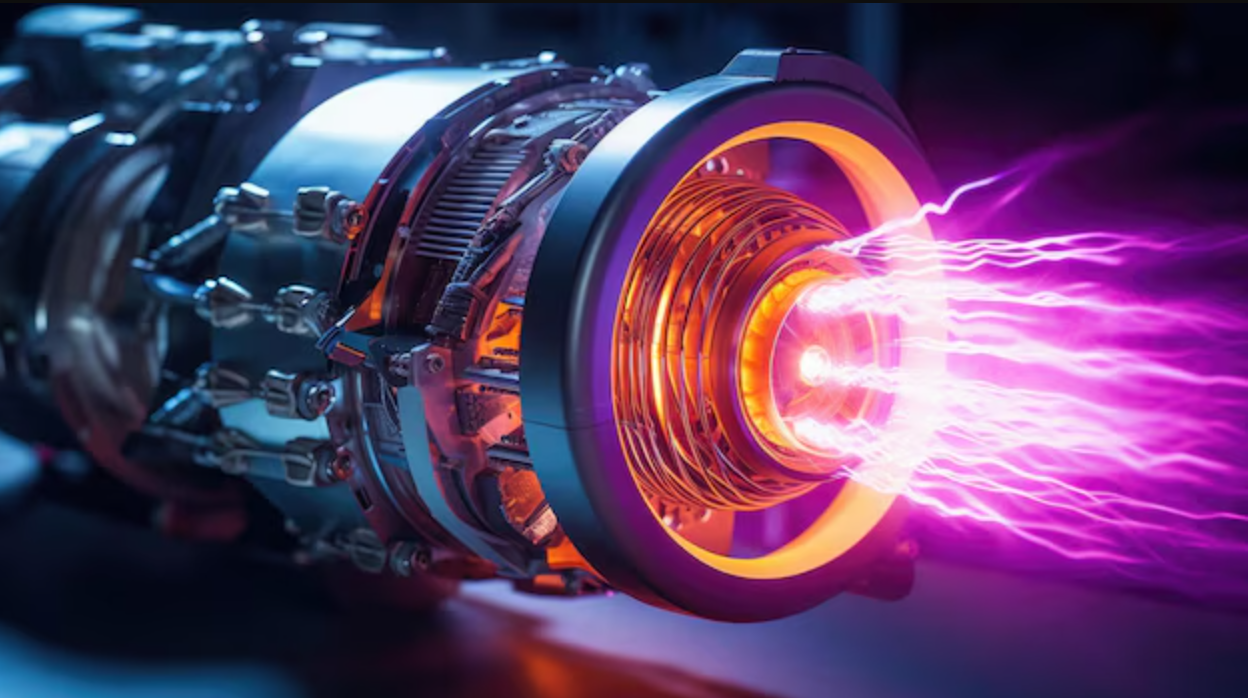
Professor Jau Tang and his staff at Wuhan University have developed a prototype jet engine powered by microwave air plasmas, providing thrust with out fossil fuels. This revolutionary method might remodel air journey by eliminating carbon emissions.
“Our work goals to resolve international warming issues by changing fossil gasoline combustion engines,” Tang defined. “With our design, there isn’t a carbon emission to trigger greenhouse results and international warming.”
How Plasma Powers the Engine
Plasma, the fourth state of matter, consists of charged particles like ions and electrons. Found naturally within the solar and lightning, it will also be generated in managed environments. Tang’s engine harnesses this state of matter by a complicated course of involving air compression and microwave expertise.
- Air Compression: The system begins by drawing in atmospheric air, which is then compressed to excessive pressures utilizing a turbine compressor. This compressed air supplies the mandatory density for efficient plasma era.
- Microwave Ionization Chamber: The compressed air flows right into a quartz tube fitted with a microwave ionization chamber. Microwaves, working at 2.45 GHz—the identical frequency utilized in microwave ovens—are directed into this chamber.
- Ionization: Inside the chamber, the high-frequency microwaves excite the air molecules, stripping electrons from the atoms and making a plasma state. The ensuing plasma reaches temperatures exceeding a number of thousand levels Celsius.
- Jet Thrust Generation: The high-temperature plasma quickly expands because it exits the ionization chamber. This growth produces a jet thrust able to lifting a 1-kilogram metal ball, demonstrating thrust comparable to traditional jet engines.
Tang’s method differs from different plasma propulsion techniques, akin to these utilized by NASA. For instance, NASA’s xenon-based plasma thrusters, like these on the Dawn spacecraft, work effectively within the vacuum of area however are ineffective in Earth’s ambiance as a result of their low thrust output. Tang’s design overcomes this limitation through the use of atmospheric air, making it possible for terrestrial and airborne purposes.

The Road to Scalable Plasma Jets
While the prototype is promising, scaling it to energy massive plane presents distinctive challenges. The present design requires megawatt-level microwave sources and superior power storage techniques able to delivering steady excessive energy.
“For a big jumbo jet, improvement might take one other decade,” Tang estimated. Scaling up entails integrating a number of plasma jet modules in a parallel configuration. This would enhance the general thrust whereas sustaining effectivity.
The prototype already achieves a jet strain of 24,000 newtons per sq. meter with 400 watts of energy, akin to industrial plane engines. However, bigger plane would require considerably greater energy outputs, which calls for developments in battery expertise.
Tang believes smaller-scale purposes, akin to heavy-duty drones or pilotless cargo planes, might grow to be operational inside 5 years. These plane can be supreme for logistics and supply companies, decreasing emissions within the transportation sector.

However, even for these smaller purposes, challenges stay. The excessive power density required for sustained flight signifies that present battery applied sciences should evolve to be lighter and extra environment friendly. Weight is a crucial concern, as heavy batteries might negate the advantages of this zero-emission propulsion system.
Addressing Engineering Challenges
Another hurdle is thermal administration. Plasma engines generate excessive warmth, which may injury engine elements over time. Tang’s staff is investigating superior supplies and cooling techniques to mitigate these results.
“We nonetheless want to enhance the engine’s effectivity and handle the affect of excessive temperatures on the gear,” Tang famous. “Managing the warmth and making certain sturdiness beneath steady operation are our subsequent huge challenges.”
Additionally, attaining secure and managed thrust throughout totally different flight circumstances is essential. The staff is optimizing the stream dynamics inside the ionization chamber to make sure constant efficiency.
A Vision for the Future of Air Travel
Despite the challenges, Tang stays optimistic. His analysis has garnered consideration from the worldwide scientific neighborhood, with many consultants recognizing its potential to revolutionize aviation. If profitable, plasma jet engines might result in a brand new period of sustainable air journey, free from the environmental and geopolitical constraints of fossil fuels.
“Our outcomes display {that a} microwave air plasma jet engine may very well be a viable different to traditional fossil gasoline engines,” Tang mentioned.

While it might take years earlier than you see plasma-powered planes within the sky, the muse is being laid for a future the place aviation is cleaner, quieter, and extra sustainable. Tang’s groundbreaking work not solely guarantees an answer to local weather change but additionally redefines what’s potential in propulsion expertise.




