Black holes are terrifying, monstrous objects with immense gravity that causes them to eat every thing that crosses their occasion horizons.
Yet the physics-breaking energy of the space-time ruptures can be a part of their draw — sucking in scientists who wish to research the function of black holes in sculpting galaxies and people trying to find a unified concept of gravity. Here are essentially the most monstrous black gap findings of the yr.
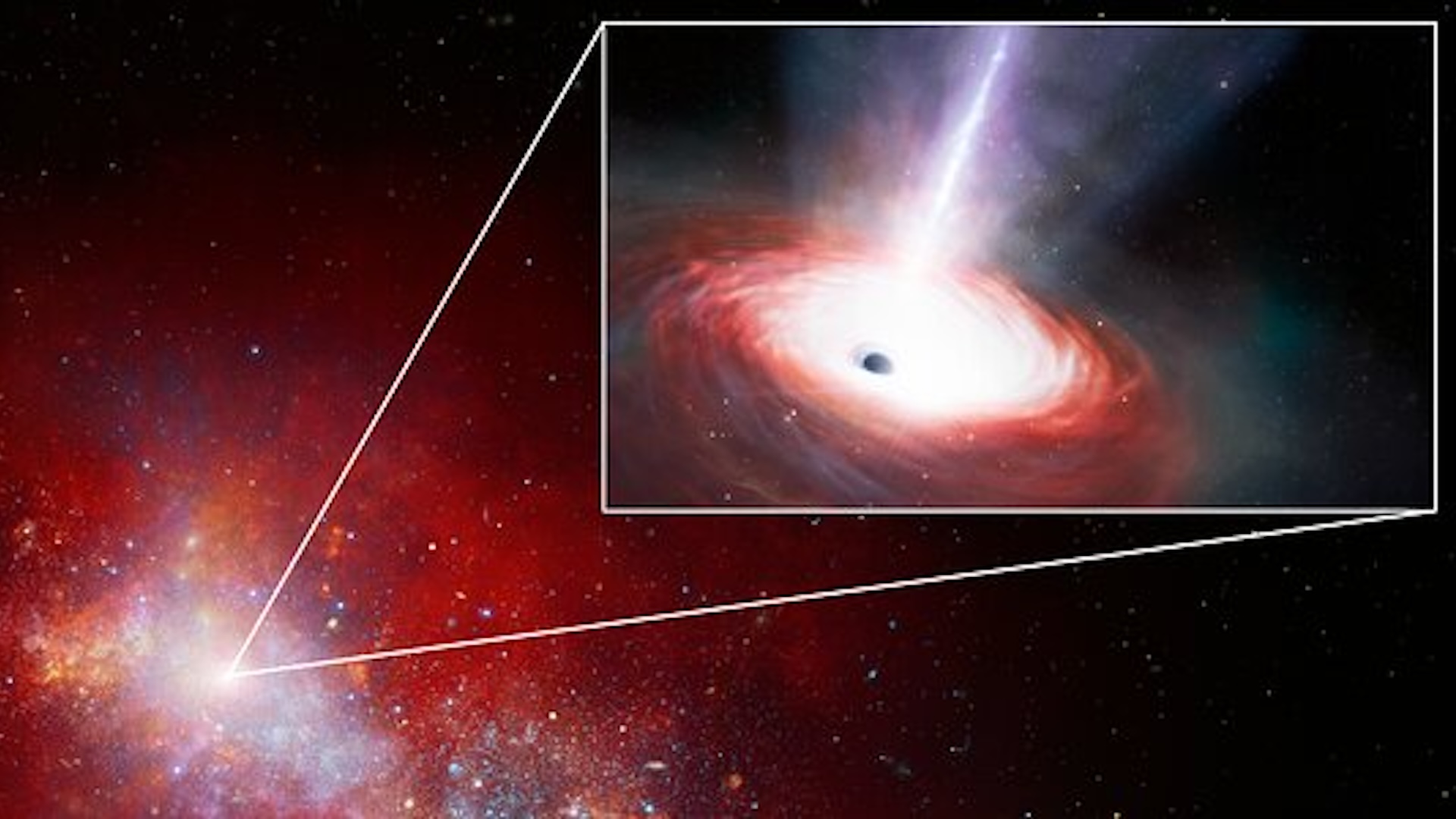
Scientists spot an ultra-rare “lacking hyperlink” black gap hiding within the Milky Way’s heart
The recognized black holes that populate the universe fall into two varieties: these up to some dozen instances the mass of the solar and their supermassive counterparts that may weigh as much as 50 billion photo voltaic lots. But precisely how the previous developed into the latter is unclear, particularly as there have but to be any confirmed sightings of black holes of their awkward intermediate phases.
Enter a new intermediate black gap candidate, which astronomers noticed contained in the IRS 13 star cluster, only a tenth of a light-year from Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black gap on the coronary heart of the Milky Way galaxy. If scientists can verify its existence, it may give important clues to how black holes evolve.
A feasting supermassive black gap is consuming materials 40 instances sooner than ought to be potential
This yr, scientists discovered one other clue to how supermassive black holes develop to their unimaginable scales, within the type of the gluttonous monster LID-568.
The James Webb Space Telescope noticed the black gap because it appeared simply 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang, and it was gobbling materials 40 instances sooner than its theoretical feeding restrict (referred to as the Eddington restrict). The discovery may clarify why so many big black holes seem so early within the universe’s historical past.
“Impossible” black holes found by the James Webb telescope might lastly have a proof
The discovering about LID-568’s feeding frenzy was removed from the final phrase on early supermassive black gap formation. Theoreticians additionally proposed how black holes got here to be seeded throughout the universe with out, as they sometimes do as we speak, rising from useless stars: by quickly collapsing pockets of gasoline that fashioned primordial black holes.
Most of those tiny singularities evaporated, in line with the brand new speculation, however the ones that survived gorged and merged at a breakneck tempo to succeed in their huge scales.
Tiny black holes could possibly be hollowing out planets and zipping by way of our our bodies
Another theoretical proposal about primordial black holes additionally made waves this yr: the suggestion that they could nonetheless exist. Perhaps they’re hollowing out planets and zipping by way of our our bodies and buildings, leaving solely microscopic traces.
If bits of tiny black holes swarming throughout the cosmos might be discovered, they might be instant candidates for a lot of the lacking matter that appears to exert a gravitational pull but barely interacts with gentle.
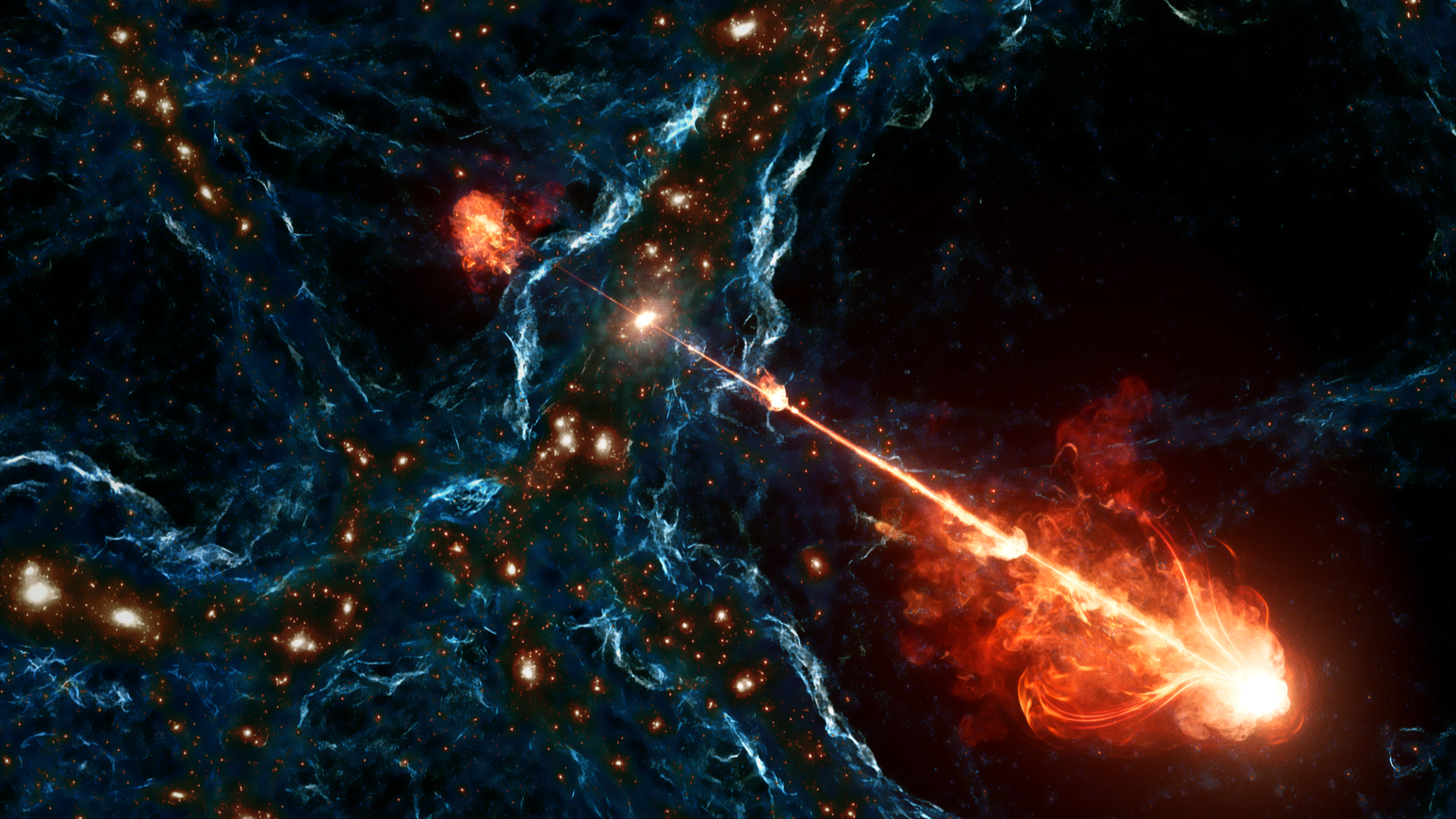
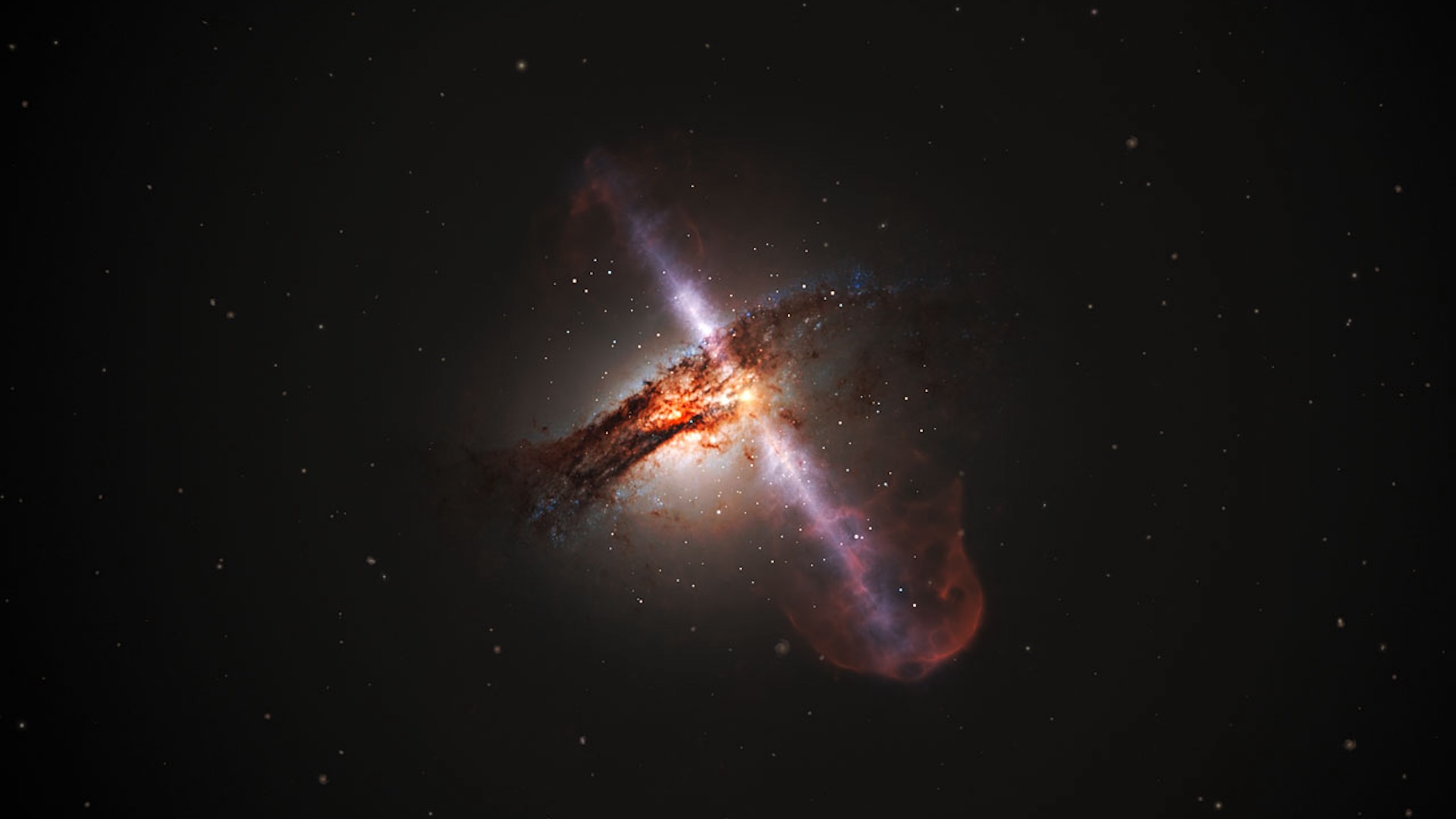
Biggest black gap jets ever seen are so long as 140 Milky Ways
Some black holes spew infalling matter out once more, forming gigantic, near-light-speed plasma jets that may lengthen for a whole lot of light-years. But one black gap jet pair astronomers noticed — named Porphyrion, after a large in Greek mythology — actually took the cake: At 23 million light-years in size, the pair is so long as 140 Milky Way galaxies laid finish to finish.
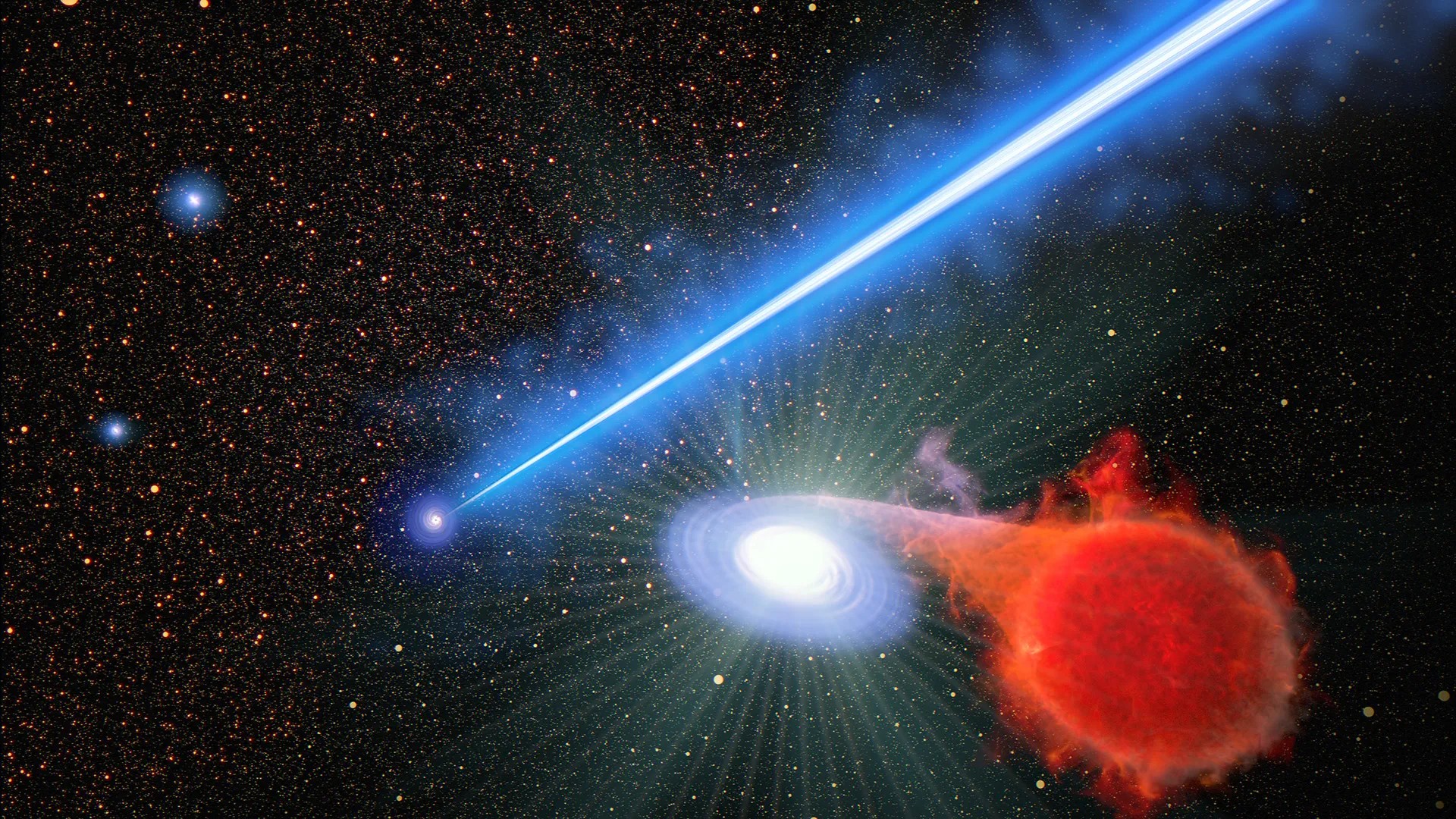
Black gap “blowtorch” is inflicting close by stars to blow up
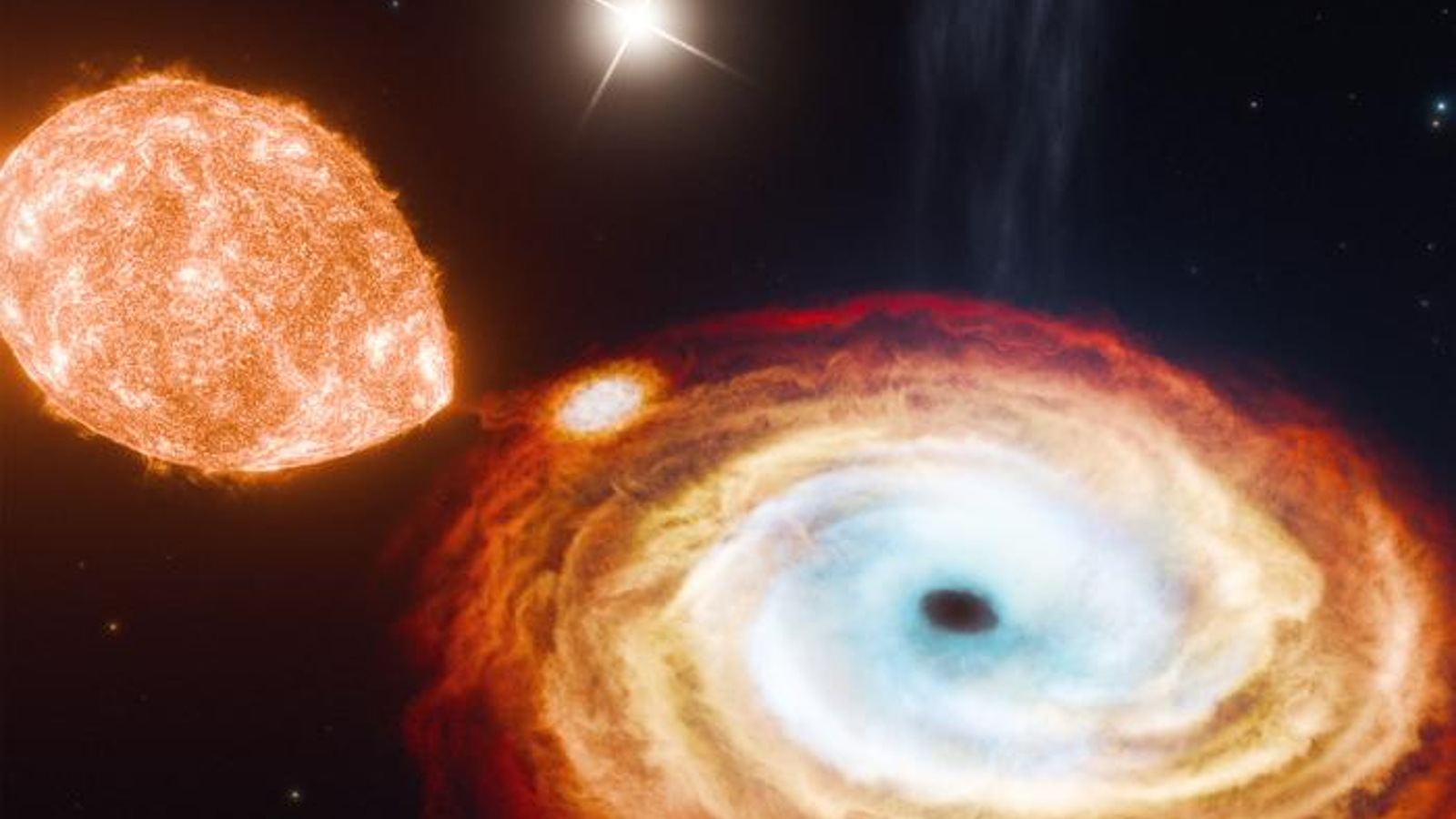
Black gap jets aren’t simply unbelievable options. They’re a strong — but nonetheless mysterious — pressure for the cosmic monsters to form the broader universe. For the primary time, researchers have noticed a black gap jet inflicting stars in its neighborhood to burst in explosions referred to as novas.
Because the celebs weren’t immediately hit by the beam, precisely how the jet is inflicting the celebs to pop is unknown. By trying to find solutions, astronomers may achieve a greater understanding of how black holes have an effect on even extraordinarily distant environment.
Astronomers uncover why some black holes have a “heartbeat”
While feeding, black holes can warmth up their “meals” to immense temperatures to launch huge X-ray flares that final tens of millions of years. But inside these flares lurks one other, unusual sign: an everyday pulse of sunshine that resembles a heartbeat. By finding out one of many flares, astronomers now assume they’ve a proof for black gap heartbeats: They’re produced by shock waves that ripple by way of black holes’ meals as they feast.
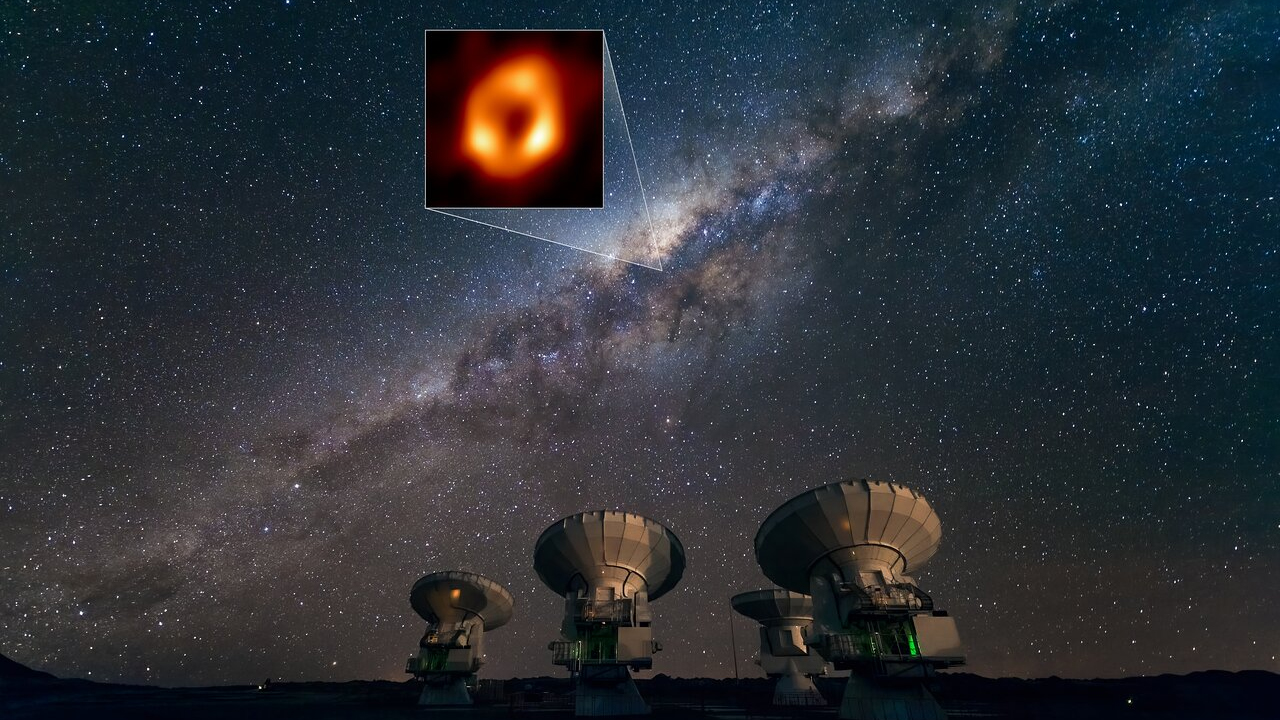
Event Horizon Telescope reveals why our galaxy’s black gap is spinning so weirdly
Our galaxy’s central black gap, Sagittarius A*, is a gargantuan tear in space-time that’s 4 million instances the mass of the solar and 14.6 million miles (23.5 million kilometers) extensive. But these are fairly commonplace proportions for a black gap of this scale. What is uncommon about Sagittarius A* is that it is spinning surprisingly quick and it is out of kilter with the remainder of the Milky Way.
This yr, utilizing the Event Horizon Telescope, which in 2022 captured the first picture of our galaxy’s black gap, scientists discovered the reply: Sagittarius A* was seemingly born from a huge collision between two large black holes, and its lopsided rotation is a key signal of its violent origins.
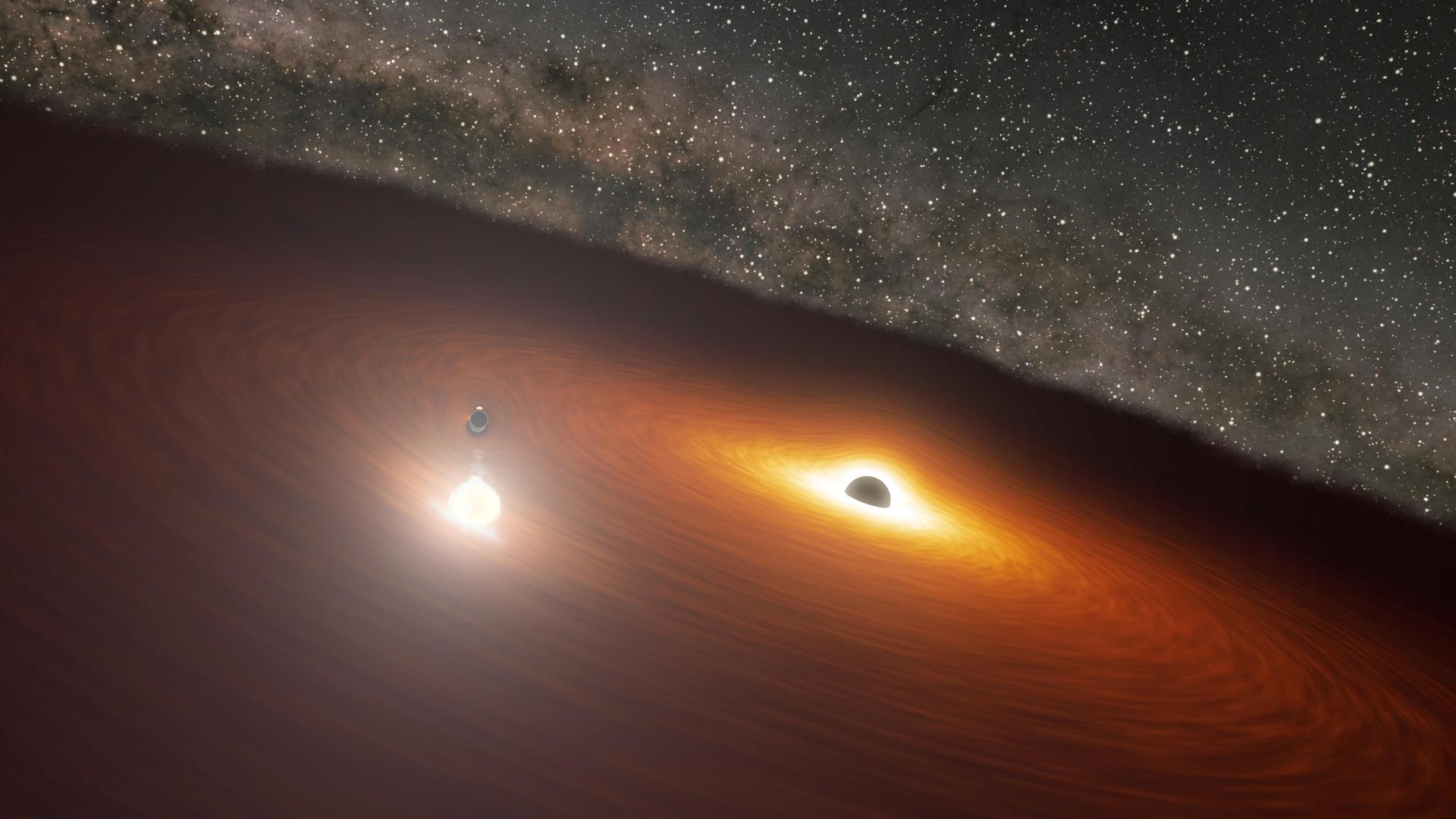
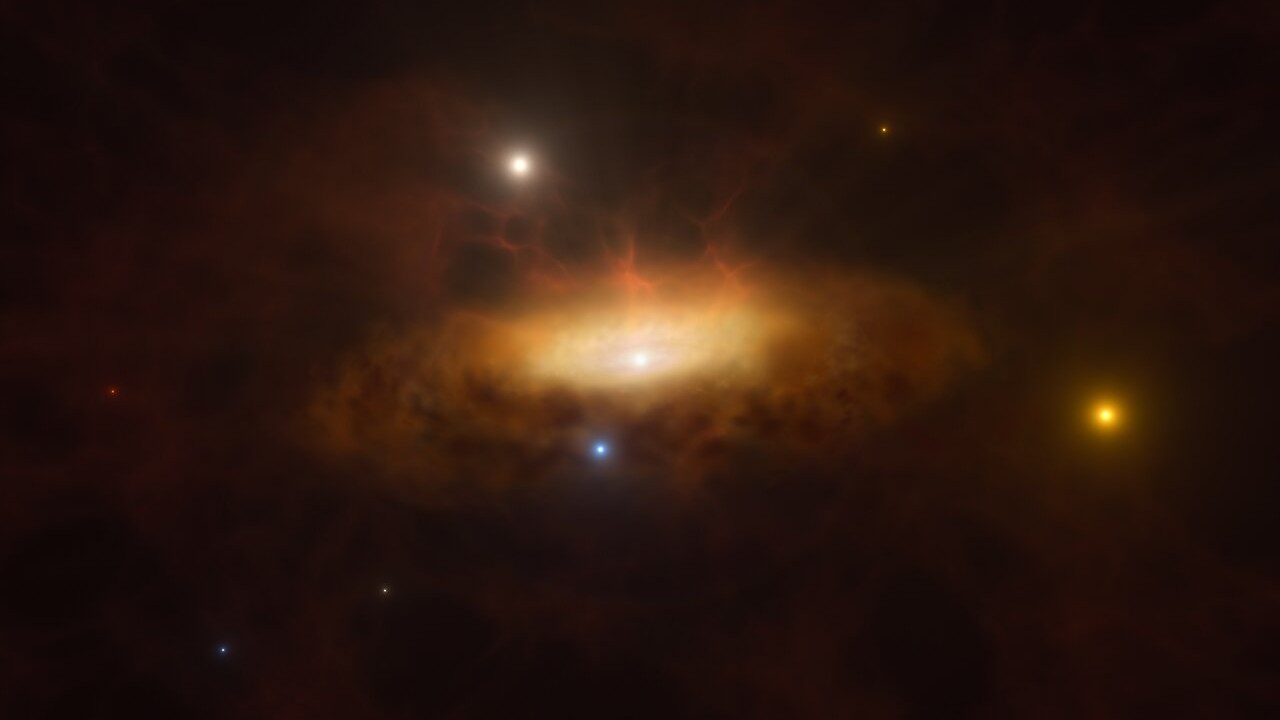
Scientists spot the primary black gap “triple” system
Many black holes exist in binary methods, orbiting a star companion, however researchers have now noticed one orbited by two stars, making it the primary black gap triple system ever seen. Beyond creating a wholly new class in its personal proper, the invention has critical implications for black gap formation.
Black holes that exist in binary methods are sometimes thought to have emerged from the gravitational collapse of a star. But astronomers say this triplet may supply firsthand proof of black holes immediately collapsing from gasoline clouds.
Dormant black gap roars to life
Black holes are sometimes both energetic and consuming materials round them, or dormant as a result of they’ve already swallowed every thing of their midst. It’s uncommon to see black holes shift between the 2 states. But astronomers have now noticed a black gap that is waking up after an extended slumber.
The causes for the black gap’s reactivation stay unclear, however astronomers hypothesize that it might have begun to seize new materials. Alternatively, the sunshine coming from close to the space-time singularity star that it has snared and exploded.