Regular ScienceAlert readers will doubtless understand how pervasive microplastics are – entering into human tissue, ancient rock, and bottled water – however it might come as a shock to find simply what number of of those tiny fragments can lurk inside a single tea bag.
A brand new research led by researchers from the Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB) in Spain discovered that particular person tea luggage can launch billions of micro- and nanoplastic (MNPL) particles in each millimeter of water they’re dunked into.
Those figures might sound surprisingly excessive, however they’re in keeping with earlier analysis wanting on the mixture of plastics and excessive warmth, similar to food containers put in the microwave. It’s a sobering reminder of the prevalence of MNPLs.
“We have managed to innovatively characterize these pollution with a set of cutting-edge methods, which is an important device to advance analysis on their doable impacts on human well being,” says microbiologist Alba García-Rodríguez, from UAB.
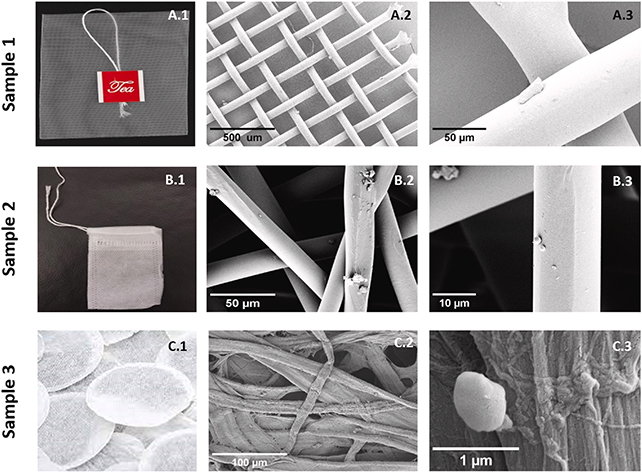
Earlier studies have raised issues concerning the amount and potential well being influence of artificial particulates from tea luggage, and right here the researchers needed to be as thorough as doable, utilizing a collection of tea luggage offered commercially.
Using laser methods to measure the velocity and scattering of sunshine gave a extremely correct image of the chemical and bodily properties of particles launched from the tea luggage.
Three sorts of tea luggage had been examined. Those made primarily from polypropylene launched about 1.2 billion particles per milliliter, averaging 136.7 nanometers in dimension. Cellulose luggage launched on common 135 million particles per milliliter, round 244 nanometers in dimension. The nylon-6 teabags sometimes launched 8.18 million particles per milliliter, averaging 138.4 nanometers in dimension.
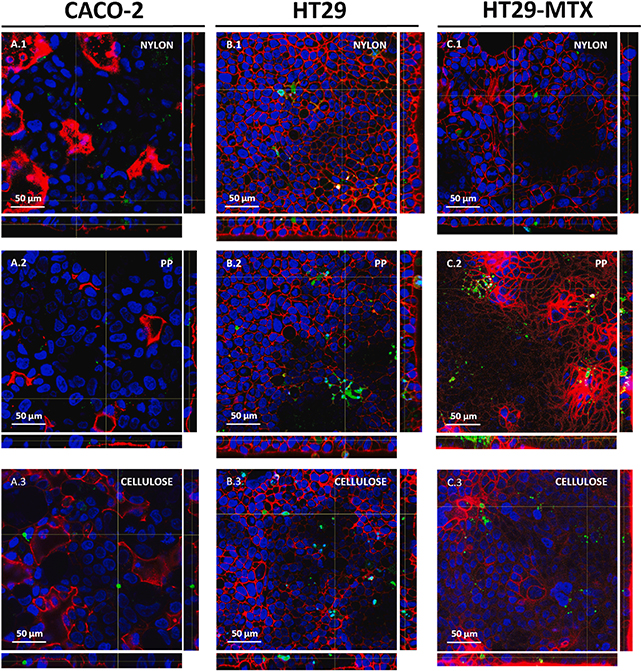
The researchers additionally examined how the MNPL particles interacted with human intestinal cells, discovering that in mucus-producing cells the absorption ranges had been sufficient for the plastics to succeed in the cell nucleus – a helpful discovery by way of assessing the impacts on well being of the plastics now floating via our our bodies.
“The polymer composition of MNPLs considerably influences their organic interactions, resulting in diversified focusing on and results on organs, tissues, and cells,” write the researchers of their printed paper.
“These variations can lead to particular accumulation patterns, toxicity profiles, immune responses, and long-term well being results similar to genotoxicity and carcinogenicity.”
The analysis workforce is looking for extra to be carried out to standardize using plastics in meals packaging as a way to safeguard public well being. While a whole lot of questions stay concerning the impacts, mounting proof exhibits that the rising presence of tiny plastic particles might put ecosystems and our own health in danger.
It’s thought that microplastics and nanoplastics might intrude with regular cell operations and make infections extra doubtless. We’ve also seen plastics within the intestine related to situations like inflammatory bowel illness (IBD).
“As the utilization of plastics in meals packaging continues to rise, scientific analysis and policymaking should deal with the challenges posed by MNPL contamination to make sure meals security and client well-being,” write the researchers.
The analysis has been printed in Chemosphere.




