Humans right now reside longer than ever before, however what number of of these added years are spent in good well being?
A knowledge-crunching survey protecting 183 member nations of the World Health Organization has now confirmed what some scientists feared: whereas years are being added to most individuals’s lives, wholesome life isn’t being added to most individuals’s years.
Researchers on the Mayo Clinic discovered that individuals world wide in 2019 have been residing 9.6 years of life burdened by incapacity or illness – a rise of 13 % from 2000.
In that very same timeframe, world life expectancy has elevated 6.5 years, and but health-adjusted life expectancy has solely elevated 5.4 years.
In the US, the hole between lifespan and ‘healthspan’ is rising significantly large.
Between 2000 and 2019, life expectancy within the US elevated from 79.2 to 80.7 years for ladies, and from 74.1 to 76.3 years for males.
When adjusting for wholesome years of added life, nonetheless, the span solely elevated by 0.6 years amongst males. And amongst ladies, whereas health-adjusted life expectancy fluctuated barely over time, in 2019 it matched the determine seen in 2000.
The increasing hole means if an American girl lived to the anticipated 80.7 years of age, the final 12.4 years of her life would on common be impacted by illness or incapacity.
According to public well being researchers Armin Garmany and Andre Terzic, the healthspan-lifespan hole within the US is 29 % greater than the worldwide common.
“The information present that good points in longevity will not be matched with equal advances in wholesome longevity. Growing older usually means extra years of life burdened with illness,” says Terzic, a cardiovascular well being researcher on the Mayo Clinic.
“This analysis has necessary follow and coverage implications by bringing consideration to a rising risk to the standard of longevity and the necessity to shut the healthspan-lifespan hole.”

The outcomes align with earlier research from world wide, which generally take into account one nation at a time, and which counsel that whereas ladies tend to live longer than males, additionally they accrue more unhealthy years of life, principally from persistent well being situations.
In gentle of those developments, the WHO lately introduced a brand new metric referred to as well being life expectancy (HALE) to attempt to measure the burden of illness and incapacity in older age, particularly after 60.
In 2020, WHO and the United Nations declared a 10-year world plan of motion. In 2022, officers wrote that to “guarantee older individuals will not be left behind, there’s a urgent have to strengthen measurement and deal with the information gaps.”
Researchers on the Mayo Clinic have now responded to that decision.
In a evaluation of the final twenty years, Garmany and Terzic have highlighted “a chasm between advances made in longevity, a conventional measure of life expectancy, and wholesome longevity, a recent indicator of amount and high quality of life.”
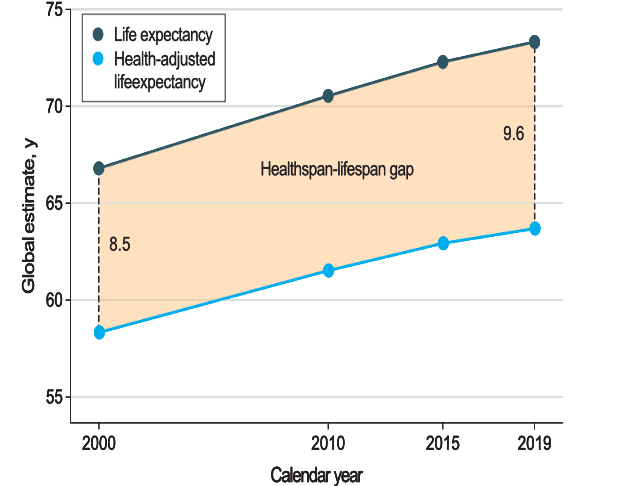
The widening hole between these two measures is now confirmed as a world development, and whereas it is a common drawback, it is going to should be addressed in a multifaceted method, from nation to nation, and between totally different teams of individuals.
For occasion, the hole in lifespan-healthspan is especially pronounced among the many feminine intercourse, who have a tendency to hold a better burden of noncommunicable ailments, like musculoskeletal, genitourinary, and neurological ailments later in life.
The largest healthspan-lifespan gaps have been noticed within the US (12.4 years), Australia (12.1 years), New Zealand (11.8 years), the UK (11.3 years), and Norway (11.2 years).
Meanwhile, the smallest gaps have been seen in Lesotho (6.5 years), the Central African Republic (6.7 years), Somalia (6.8 years), Kiribati (6.8 years), and Micronesia (7.0 years).

Given that poor well being was analyzed utilizing a blanket measurement of illness and incapacity, researchers say the following step is to dig additional, determine which teams of individuals are struggling essentially the most of their later years, and the way we are able to greatest assist them age with dignity.
“The widening healthspan-lifespan hole is a world development, as documented herein, and factors to the necessity for an accelerated pivot to proactive wellness-centric care techniques,” the 2 authors conclude.
The examine was printed in JAMA Network Open.




