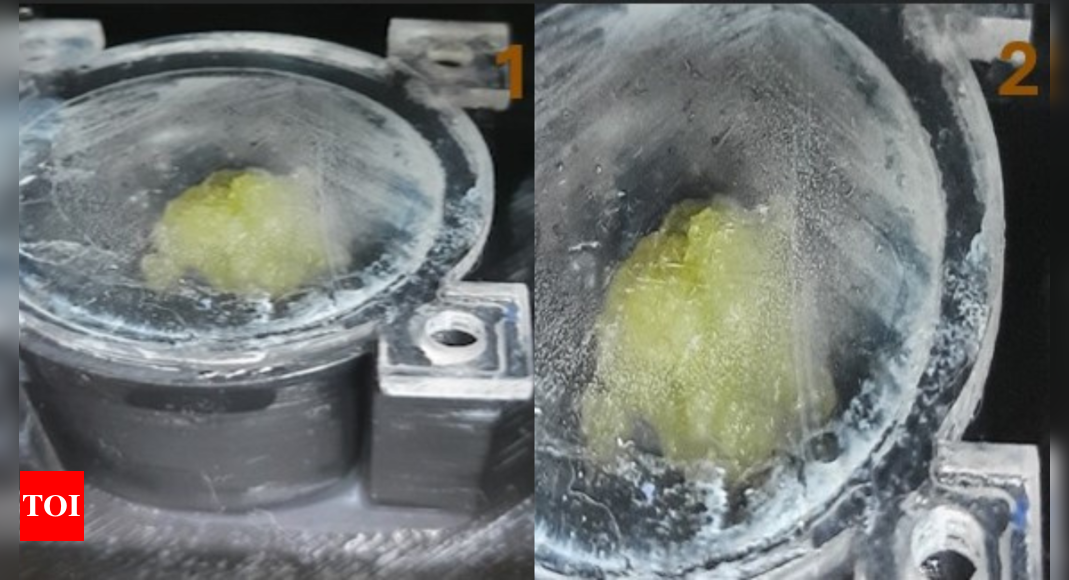
BENGALURU: Initial outcomes from India’s first non-Isro organic house experiment reveal profitable development of spinach tissue in zero gravity situations, marking a big milestone for space-based agriculture analysis.
The spinach callus tissue — despatched by Amity University, Mumbai — orbiting 350km above Earth, has demonstrated development patterns akin to ground-based management samples throughout its first week in house.
“The preliminary knowledge is extraordinarily promising. Our real-time monitoring exhibits wholesome tissue growth, with all environmental parameters together with CO2 ranges, humidity, and lighting methods performing optimally,” AW Santhosh Kumar, vice-chancellor and lead scientist at Amity University Mumbai’s Center for Astrobiology, informed TOI.
The experiment, performed by means of the Amity Plant Experimental Module in Space (APEMS), is utilising an revolutionary method of rising callus tissue somewhat than conventional seeds. This methodology permits researchers to extra simply monitor adjustments in development and well being by means of colour monitoring, as any stress-induced discoloration within the vibrant inexperienced tissue will be readily detected by the module’s built-in cameras.
The college had despatched the spinach callus onboard the PSLV Orbital Experiment Module (POEM) a part of the PSLV-C60 mission that launched the 2 Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) satellites into orbit on Dec 30. TOI had reported earlier concerning the experiment being a part of the 24 experiments on POEM.
Kumar, whereas mentioning that the experimental mannequin chosen is ‘Spinacia Oleracea’, stated crops are very delicate to many environmental stimuli like mild, temperature, dietary situations, and gravity.
“The data obtained from this experiment below APEMS will present an understanding how larger crops sense the course of gravity and lightweight and ameliorate themselves to answer gravitational stress and regulate their course of development, a primary want for enhancing plant development on Earth in addition to extended spaceflight missions,” he stated.
Data collected from the orbiting module, which completes 16 revolutions round Earth each day at 28,800 km/hour, exhibits the tissue cultures are adapting effectively to the microgravity atmosphere. Photographic proof from the primary seven days in orbit confirms seen development development, matching expectations set by terrestrial experiments.
The success of this ongoing 21-day mission may have far-reaching implications for future house missions, notably for India’s proposed house station, the Bharatiya Antariksh Station or BAS. The analysis staff is particularly learning how crops sense and reply to gravitational stress, data that might show essential for establishing sustainable meals manufacturing methods in house.
The APEMS experiment employs a number of applied sciences, together with the primary 3D-printed organic payload module of its form, indigenous software program for real-time development monitoring and a classy sensor array in a miniaturised prototype.
The staff plans to make use of these preliminary findings to suggest extra intricate actual time experimentation on Isro’s human spaceflight mission and be part of the proposed house station.
In a primary, Indian college grows spinach tissue in house | India News – Times of India