Do we now have a planetary bias relating to understanding the place life can perpetuate? It’s solely pure that we do. After all, we’re on one.
However, planets will not be vital for all times, and a pair of scientists from Scotland and the USA are inviting us to rethink the notion.
We deal with planets as habitats for all times as a result of they meet the circumstances vital for all times to outlive. Liquid water, the best temperature and stress to maintain it in a liquid state, and safety from dangerous radiation are the first necessities for photosynthetic life.
But what if different environments, even ones maintained by organisms themselves, may present these requirements?
In new analysis printed within the journal Astrobiology, researchers level out that ecosystems may generate and maintain the circumstances vital for their very own survival with out requiring a planet.
The paper is titled “Self-Sustaining Living Habitats in Extraterrestrial Environments.” The authors are Robin Wordsworth, Professor of Earth and Planetary Sciences at Harvard, and Charles Cockell, Professor of Astrobiology within the School of Physics and Astronomy on the University of Edinburgh.
“Standard definitions of habitability assume that life requires the presence of planetary gravity wells to stabilize liquid water and regulate floor temperature,” they write. “Here the implications of stress-free this assumption are evaluated.”
Wordsworth and Cockell write that biologically generated limitations and buildings can mimic the planetary circumstances that allow life with out the planet. They can let mild in for photosynthesis whereas blocking UV mild. They may forestall risky loss whereas in a vacuum and preserve the temperature and stress vary required for water to stay in a liquid state.
“Biologically generated limitations able to transmitting seen radiation, blocking ultraviolet, and sustaining temperature gradients of 25-100 Okay and stress variations of 10 okayPa in opposition to the vacuum of area can enable liveable circumstances between 1 and 5 astronomical models within the Solar System,” they write.
“To perceive the constraints on life past Earth, we are able to begin by reviewing why our house planet is an efficient habitat for all times within the first place,” write the authors.
Earth does extra than simply present liquid water and safety from radiation. It’s a whole system with layers of interacting complexity.
The planet’s floor is uncovered to an simply accessible supply of power from the Sun that drives the entire biosphere. The parts we consider as important for all times can be found, although generally restricted: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, and sulfur. They cycle via the biosphere by way of volcanism and plate tectonics and grow to be out there once more.
Earth can also be oxidizing within the ambiance and on the floor, and decreasing in different areas like sediments and the deep subsurface. This permits for “the exploitation of redox gradients for metabolic functions,” the authors clarify.
Those circumstances do not exist elsewhere. Astrobiology targets the Solar System’s frozen moons due to their heat, salty oceans. But have they got nutrient cycles?
Low-mass objects within the outer Solar System have ample floor space, however the Sun’s power is weak. They’re unlikely to have the ability to maintain onto their atmospheres, so the right stress and temperature for liquid water are out of attain. They’re additionally unprotected from UV radiation and cosmic rays.
“To persist past Earth,” the authors write, “any dwelling organism should modify or adapt to its surroundings sufficient to surmount these challenges.”
The authors write that organic supplies right here on Earth can already try this. It’s believable that ecosystems may develop the circumstances for their very own survival, and if photosynthetic life can do it within the vacuum of area, then so may we. It can be a significant profit for human area exploration.
It begins with water, and relating to liquid water, scientists consult with its triple level. A triple level is a thermodynamic reference level that explains part transitions and the way water behaves underneath totally different pressures and temperatures.
“The minimal stress required to maintain liquid water is the triple level: 611.6 Pa at 0?C (273 Okay),” the researchers clarify. That quantity rises to some okayPa between 15 to 25 Celsius.
Cyanobacteria can develop with air headspace pressures of 10 okayPa, as long as the sunshine, temperature and pH are in the best ranges. The query is, do any dwelling issues that we all know of generate partitions that may preserve 10 okayPa?
“Internal stress variations of order 10 okayPa are simply maintained by organic supplies and actually frequent in macroscopic organisms on Earth,” the authors write. “The blood stress improve from the pinnacle to the ft of a 1.5-m tall human is round 15 okayPa.”
Seaweed may maintain inner float nodule pressures of 15-25 okayPa by releasing CO2 from photosynthesis.
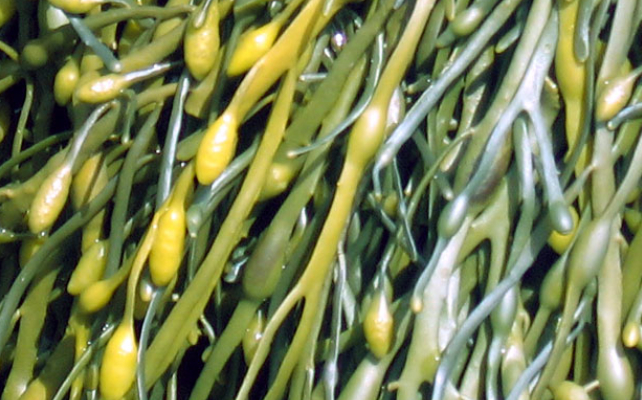

Temperature is the subsequent consideration relating to liquid water. Earth maintains its temperature via the atmospheric greenhouse impact. But small rocky our bodies, for instance, are unlikely to copy this.
“Hence, a biologically generated habitat should obtain the identical impact by way of solid-state physics,” write the authors.
Incoming power and outgoing power must be balanced, and a few organisms on Earth have developed to keep up this steadiness.
“Saharan silver ants, for instance, have developed the flexibility to reinforce each their floor near-infrared reflectivity and their thermal emissivity, permitting them to outlive in ambient temperatures above the vary of all different identified arthropods,” Wordsworth and Cockell write. It permits them to outlive by foraging within the warmth of the day when predators should keep out of the Sun.
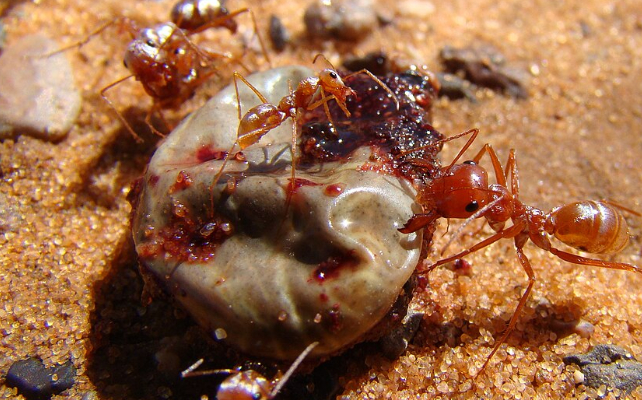

Humans have made silica aerogels with extraordinarily low density and thermal conductivity. While there are not any direct organic equivalents, the authors write that “many organisms do exist in nature that produce advanced silica buildings.”
In truth, some diatoms can produce silica buildings by manipulating silica particles smaller than these utilized in our manufacturing processes. Aerogels manufactured from natural supplies have related traits to synthetic ones.
“Given this, it’s believable that extremely insulating supplies could possibly be produced artificially from biogenic feedstocks and even immediately by dwelling organisms,” the authors write.
The authors calculated that a lot of these buildings may preserve the best temperature and stress to keep up liquid water.
“As might be seen, sustaining inner temperature at 288 Okay is feasible for a variety of orbital distances,” they clarify. “This calculation assumes a free-floating habitat, however related issues apply to habitats on the floor of an asteroid, moon, or planet.”
Volatile loss is one other drawback. A habitat that may’t maintain onto its ambiance cannot preserve the temperature and stress vital for liquid water.
“All supplies have some permeability to atoms and small molecules, and over lengthy timescales, the vacuum of area represents an primarily everlasting sink for risky species,” the authors clarify.
This might be solved by the identical limitations that preserve stress and temperature. “Inhibition of risky escape can be most simply achieved by the identical a part of the habitat wall answerable for sustaining the stress differential essential to stabilize liquid water,” write the authors.
The authors additionally think about the consequences of UV radiation. Radiation might be lethal, however there are examples of life right here on Earth which have developed to determine it out.
“However, it’s simply blocked by compounds equivalent to amorphous silica and lowered iron, which attenuate UV in silicified biofilms and stromatolites as we speak with out blocking the seen radiation wanted for photosynthesis,” they write.
The availability of photo voltaic power for photosynthesis probably is not a lot of a barrier in lots of elements of the Solar System. The authors level out that Arctic algae grows in extraordinarily weak mild underneath the ice.
Some kind of nutrient cycle can be required, identical to on Earth. “Long-term, a further consideration is the flexibility of a closed-loop ecosystem to course of waste merchandise equivalent to recalcitrant natural matter and to maintain inner redox gradients,” clarify the authors.
The excessive warmth in Earth’s inside will get it carried out, however with out these extremes, “a completely closed-loop ecosystem in area would require some inner compartmentalization to ascertain chemical gradients and specialist biota able to breaking down recalcitrant waste merchandise,” they write.
In their paper, the authors cowl different components like cell dimension and the components that restrict the scale of unicellular organisms and bigger, extra advanced organisms. They conclude that totally autonomous dwelling habitats cannot be dominated out.
“Nonetheless, a completely autonomous system able to regeneration and development is seemingly not prohibited by any bodily or chemical constraints and is due to this fact attention-grabbing to think about a bit of additional,” they write.
It’s potential so long as the system can regenerate its partitions. The authors level out that current photosynthetic life can already produce amorphous silica and natural polymers. These supplies may function partitions and no less than present that there is a pathway the place organisms may evolve to create habitat partitions.
“A extra autonomous dwelling habitat would have the ability to develop its personal wall materials, simply as plant cells regenerate their very own partitions on the micrometre scale,” they clarify.
We are inclined to suppose that if life exists elsewhere, it follows the identical evolutionary pathway because it did right here on Earth, however that will not be true. “Because the evolution of life elsewhere might have adopted very totally different pathways from on Earth, dwelling habitats may additionally exist exterior conventional liveable environments round different stars, the place they’d have uncommon however doubtlessly detectable biosignatures,” the authors write.
The authors ask, “Could the type of organic buildings we focus on right here evolve naturally, with out clever intervention?” They argue that non-sentient life can maintain the entire circumstances essential to survive in extraterrestrial environments.
“Life on Earth has not but carried out this, though it has actually tailored to an more and more wide selection of environmental circumstances over time,” they conclude. “Investigating the plausibility of various evolutionary pathways for all times underneath various planetary boundary circumstances might be an attention-grabbing subject for future analysis.”
This article was initially printed by Universe Today. Read the unique article.




