Researchers have recognized a brand new species of historic people, which they’ve named Homo juluensis, which means “large head,” primarily based partly on a really massive cranium present in China.
But what is that this new species, and the way does it assist paleoanthropologists perceive hominin variation within the Middle Pleistocene epoch about 300,000 to 50,000 years in the past?
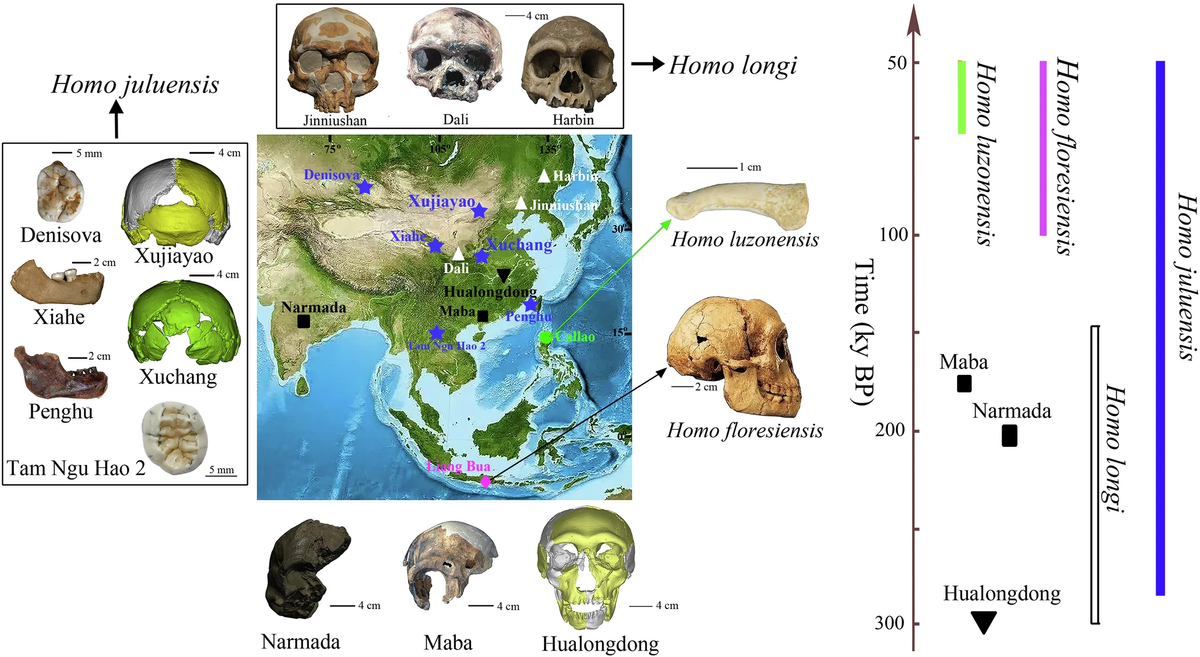
After our H. sapiens ancestors developed roughly 300,000 years in the past, they shortly unfold out of Africa and into Europe and Asia. For a long time, paleoanthropologists have tried to determine how hominins had been evolving previous to the arrival of contemporary people, significantly between about 700,000 and 300,000 years in the past, when a number of different early people existed. For occasion, anthropologists have discovered fossils from species like H. heidelbergensis in western Europe and Homo longi in central China, although not everybody agreed every of those represented a separate species. These fossils have additionally been lumped into catch-all phrases like “archaic H. sapiens” and “Middle Pleistocene Homo,” and are generally informally known as “the muddle within the Middle.”
Writing concerning the fossil hominin proof from China within the journal The Innovation in 2023, Christopher Bae, an anthropologist on the University of Hawai’i at Mānoa, Xiujie Wu, a paleoanthropologist on the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology on the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and colleagues wrote that persevering with to make use of these catch-all phrases has hindered makes an attempt to completely perceive the evolutionary relationships amongst our ancestors.
Related: Strange, 300,000-year-old jawbone unearthed in China might come from vanished human lineage
In a examine printed May 2024 within the journal PaleoAnthropology, Wu and Bae described a set of surprising hominin fossils that had been discovered a long time prior at Xujiayao in northern China. The cranium was very massive and vast, with some Neanderthal-like options. But it additionally had traits frequent to fashionable people and to Denisovans.
“Collectively, these fossils characterize a brand new type of massive brained hominin (Juluren) that was widespread all through a lot of jap Asia through the Late Quaternary [300,000 to 50,000 years ago],” they wrote.
Now, in a commentary printed Nov. 2 within the journal Nature Communications, Bae and Wu say that the rising fossil document in east Asia requires new terminology. Splitting “archaic Homo” on this space into at the very least 4 species — H. floresiensis, H. luzonensis, H. longi and the newly named H. juluensis — will assist researchers higher perceive the complexity of current human evolution, they argue.
The newly named H. juluensis relies on fossils that date to between 220,000 and 100,000 years in the past from Xujiayao and Xuchang, a website in central China. In 1974, excavators found greater than 10,000 stone artifacts and 21 hominin fossil fragments representing about 10 totally different people at Xujiayao. All of the cranial bones present that these hominins had massive brains and thick skulls. The 4 historic skulls from Xuchang are additionally very massive and much like these of Neanderthals.
In trying on the combination of traits current in these teams of fossils, Wu and Bae determined within the May 2024 paper that “they characterize a brand new hominin inhabitants for the area, specifically Juluren, which means ‘massive head individuals’.”
Although H. juluensis is taxonomically a brand new hominin species, that doesn’t imply they had been genetically remoted. They might have been the product of mating between several types of Middle Pleistocene hominins, together with Neanderthals, they wrote, “supporting the concept of continuity with hybridization as a serious pressure shaping human evolution in jap Asia.”
Although H. juluensis isn’t but generally accepted, the title is rising on specialists.
Cyber Monday 2024
Cyber Monday digital camera offers reside: Plus, financial savings on telescopes, binoculars and stargazing equipment
You can even seize the newest reductions on science kits, air purifiers and extra, as really useful by our skilled testers and editors.
“Names are vital each in evolutionary biology and in anthropology. A reputation is a psychological instrument that allows us to speak with different individuals a few idea,” paleoanthropologist John Hawks of the University of Wisconsin–Madison wrote in a June 16 weblog put up. “I see the title Juluren not as a alternative for Denisovan, however as a method of referring to a specific group of fossils and their attainable place within the community of historic teams.”
Chris Stringer, a paleoanthropologist on the Natural History Museum in London, advised Live Science in an e-mail that his personal work with Chinese colleagues suggests the H. juluensis materials may very well match higher with H. longi. “I do not suppose having a big skull is a really helpful defining attribute,” he stated. “However, Xuchang actually does appear totally different, with extra Neanderthal-like traits, so its classification is much less sure.”
In a assertion, Bae stated that naming a brand new species helps make clear the fossil document, significantly in Asia. “Ultimately, this could assist with science communication,” he stated.