The Arctic is formed by its chilly, harsh local weather and restricted daytime throughout winter. But the usually frigid area is warming about 4 occasions sooner than the remainder of the planet, which has facilitated extra transportation and elevated improvement. To higher perceive altering human exercise within the area, scientists are wanting on the far northern latitudes at night time.
When darkness spans huge areas of the planet’s land and oceans within the nighttime hours, some indicators of human actions change into simpler to identify. Satellite observations of lights shining from buildings, roads, and different infrastructure reveal patterns of human presence and improvement.
Using nighttime satellite tv for pc information, a world workforce of researchers discovered that between 1992 and 2013, the Arctic grew to become 5% brighter per 12 months, culminating in about 605,000 sq. kilometers (234,000 sq. miles) that had reworked from darkish to lit.
“Only 15% of the lit-up areas of the Arctic through the examine interval contained human settlements like properties or condominium buildings, which tells us that many of the synthetic mild is because of industrial actions reasonably than city or residential improvement,” mentioned Zhuosen Wang, a member of the analysis workforce and a scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. The industrial improvement contains extractive industries, reminiscent of drilling for oil and gasoline and mining.
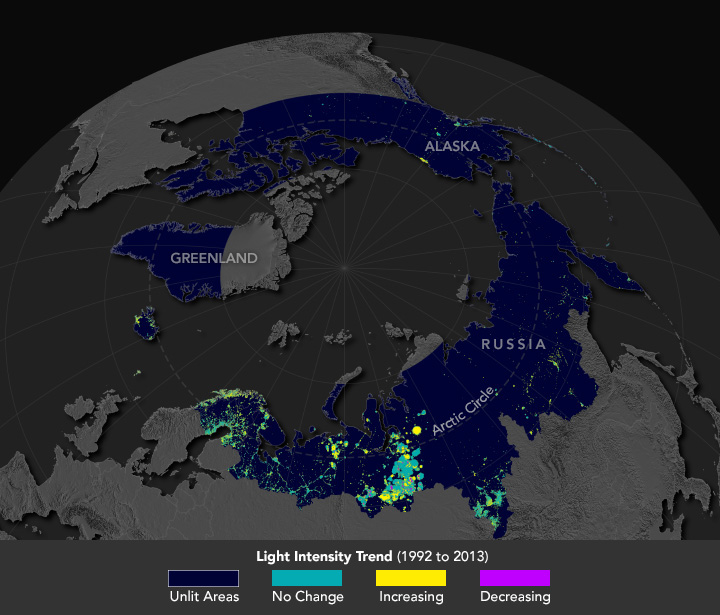
The map above reveals a pan-Arctic view of nighttime lights and locations the place the depth of synthetic lights has elevated (yellow), decreased (purple), or stayed the identical (inexperienced). The workforce used nighttime satellite tv for pc observations from the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP).
Regions of oil and gasoline extraction in northern Russia, the U.S. state of Alaska, and the European Arctic had been hotspots for synthetic mild, they discovered, whereas the Canadian Arctic largely remained darkish. The Russian Arctic had the biggest will increase in lit space (439,048 sq. kilometers) through the examine interval, particularly in Khanty-Mansi (114,426 sq. kilometers) and Yamal Nenets (107,837 sq. kilometers).

The detailed map above reveals Russia’s Khanty-Mansi area, an unlimited, swampy space within the western Siberian Plain. The area is house to the Samotlor, one of many largest oil fields on the planet, which noticed the best growth of nighttime lights through the examine interval.
Although Khanty-Mansi skilled vital growth of human exercise, there have been additionally some declines in lit-up space. “Extractive industries comply with lifecycle phases of growth and contraction,” Wang mentioned, “which is why we see reductions in synthetic lights in some locations reliant on oil, gasoline, or mining, with out vital human settlement and financial diversification.”
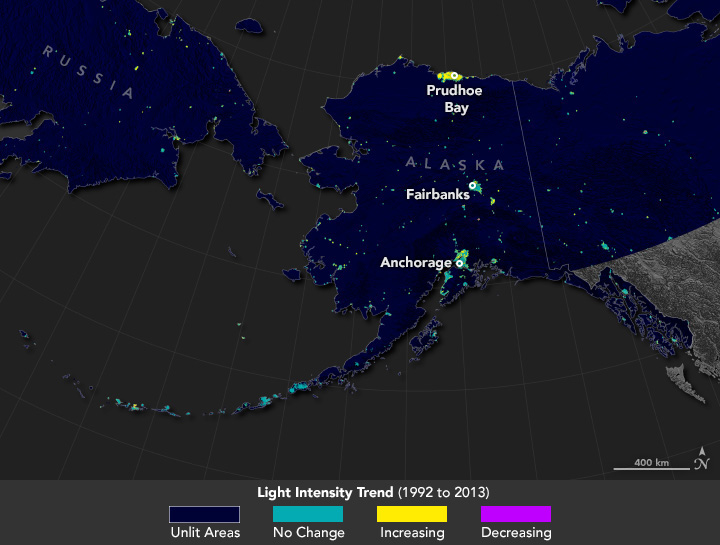
In 2013, the overall lit space in oil and gasoline extracting areas within the Russian Arctic—spanning the Khanty-Mansi, Yamal-Nenets, and Nenets areas—was 339,000 sq. kilometers (131,000 sq. miles), virtually the dimensions of Germany. The whole lit space of the European Arctic was 159,000 sq. kilometers, whereas the North American Arctic was 49,000 sq. kilometers. The analysis workforce additionally recognized mines used for extracting different minerals, such because the Red Dog Mine in distant Alaska, which was the second largest supply of zinc on the planet as of 2018.
Wang leads NASA’s Black Marble workforce, which produces pictures and composites of nighttime lights throughout the planet. The workforce makes use of information from the VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) instrument on the NASA-NOAA Suomi-NPP (Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership) satellite tv for pc, NOAA-20, and NOAA-21 satellites, that are greater decision and newer than the DMSP information used on this examine. But VIIRS typically picks up dim mild from sources just like the aurora borealis and moonlight on snow. The Black Marble workforce is working to right for such pure sources of sunshine to allow them to replace their evaluation of synthetic mild within the Arctic.
“By offering real-time, high-resolution insights, we can higher determine modifications in industrial exercise,” mentioned Miguel Román, the Deputy Director for Atmospheres at Goddard. “These analyses might help guarantee accountable useful resource administration and defend the ecosystems very important to each native and world stability.”
NASA Earth Observatory pictures by Wanmei Liang, utilizing information from Akandil, C., et al. (2024). Story by Emily Cassidy.



