A collaborative effort between researchers on the Shanghai Jiao Tong University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences led to the deployment of a simulation code on a nuclear fusion collision mannequin that has unlocked the physics behind supra-thermal ions within the burning plasma.
This helps us enhance our understanding of how nuclear fusion reactions happen and the way they are often improved.
In our bid to transition to wash vitality, nuclear fusion is a crucial part. Replicating reactions that energy the Sun right here on Earth may assist us unlock boundless vitality with out emitting planet-warming gases. To attain there, we have to first achieve getting extra vitality out of a nuclear fusion reactor than we put in.
Humanity made some progress on this path when the US’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) achieved a internet acquire of three.15 million Joules (MJ) of vitality in December 2022. To make additional advances, scientists are, nevertheless, specializing in one other NIF milestone achieved in February of 2021 – burning plasma for the primary time.
What is burning plasma?
In NIF’s strategy to harnessing fusion vitality, a gas mixture of deuterium and tritium (DT) undergoes implosion below response circumstances just like what exists within the stars. NIF refers to this strategy as inertial confinement fusion (ICF).
In ICF, when deposited vitality from alpha particles is greater than required for reaching implosion, the response combine enters a burning state that amplifies vitality densities within the plasma, often known as burning plasma.
While this state can assist us unlock fusion vitality, it additionally gives us glimpses of the circumstances of the early universe. Subsequent experiments on the NIF supplied us with extra details about these circumstances but in addition introduced discrepancies in neutron spectrum information to the fore.
Supra thermal ions
Traditionally, the habits of particles in fusion environments has been primarily based on Maxwell distributions. However, researchers discovered that this strategy neglected crucial kinetic results arising in non-equilibrium eventualities and doesn’t clarify the presence of supra-thermal ions.
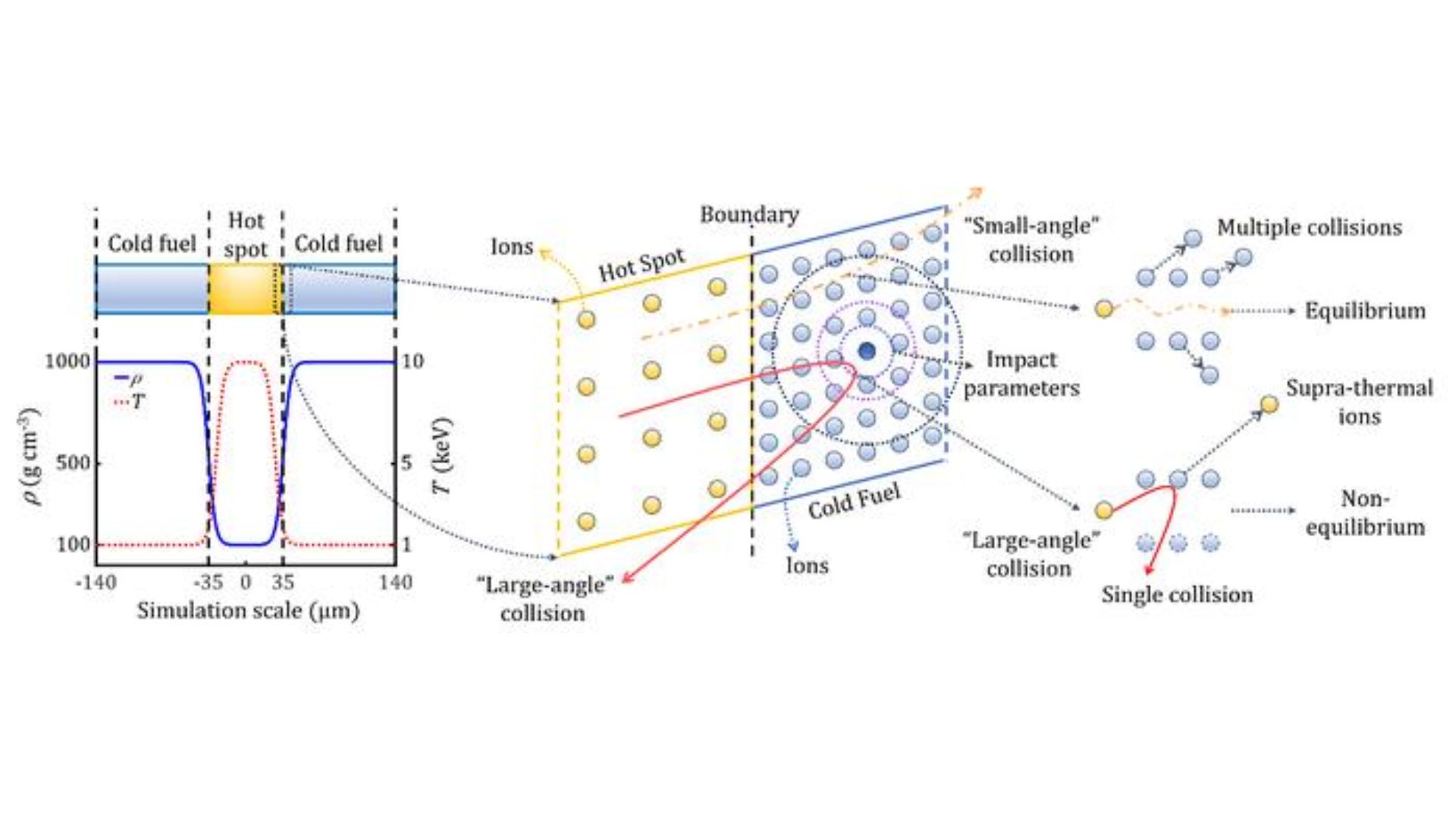
To handle this hurdle, a analysis crew led by Jie Zhang on the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a novel mannequin centered round large-angle collision dynamics, a revolutionary and multi-faceted strategy.
Employing a hybrid-particle-in-cell simulation code referred to as LAPINS, the crew performed high-precision simulations of ICF-burning plasma to achieve insights into the fusion response. They discovered that large-angle collisions promote ignition response by 10 picoseconds, which may assist enhance fusion reactions.
The simulation detected the presence of supra-thermal D ions with energies under the brink of 34 keV. This is necessary because the vitality deposition is twice that of alpha particles. The crew additionally discovered that alpha particle densities on the heart of the hotspot had been enhanced by 24 %.
The info gained from these experiments will assist us fine-tune response circumstances for fusion reactions and perceive how high-energy densities influence plasma evolution. In the long term, it will assist us acquire extra insights into the method of our universe increasing as nicely.
The analysis findings had been printed within the journal Science Bulletin.