(BIVN) – Kīlauea and Mauna Loa volcanoes usually are not erupting. The USGS Volcano Alert degree for Kīlauea is ADVISORY, and Mauna Loa is NORMAL.
Scientists have seen an uptick in exercise at Kīlauea. “Over the previous week, earthquake charges beneath Kīlauea summit and higher East Rift Zone had been greater than double that of the earlier week,” the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory wrote in a weekly exercise replace. “About 100 earthquakes had been situated beneath the summit, and about 226 had been situated within the higher East Rift Zone. Earthquake charges beneath the center East Rift Zone had been on par with the earlier week. Ground deformation charges within the summit area confirmed elevated inflation over the previous week, whereas floor deformation charges close to the September 15-20 center East Rift Zone eruption web site have slowed.”
Scientists additionally wrote an in depth Volcano Watch article on how pc monitoring can assist sound the alarm {that a} distant eruption is going on.
From this week’s article, written by USGS HVO scientists and associates:
The USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) retains its eyes on lively volcanoes in some ways. While quaint eyes and a pocket book are used when subject groups are close to a volcano, fashionable volcano observatories additionally make the most of quickly collected knowledge and computer systems to assist monitoring.
Because it may be very costly to have scientists watch the volcano knowledge streams on a 24-hour foundation, HVO computer systems are ‘educated’ to search for exercise and alert when the volcano is altering or turning into lively. They take a look at a big selection of observations together with seismic (floor shaking), infrasound knowledge (air strain), floor deformation, in addition to digicam picture assessments.
As the information from these programs enter a pc, they are often assessed as near the time of assortment as attainable. If an commentary is uncommon, the pc can ship a message to make a scientist conscious at any time of the day or night time.
At the core of many alarm programs is an often-simple pc program which seems for a change in vitality from shaking of a seismometer or a burst of sound on an acoustic sensor. If the sensor is normally quiet after which the burst of vitality happens, then this may be detected by the pc which might ship an automatic message to a scientist. This kind of vitality burst detector is named a short-term common/long-term common (STA/LTA) detector.
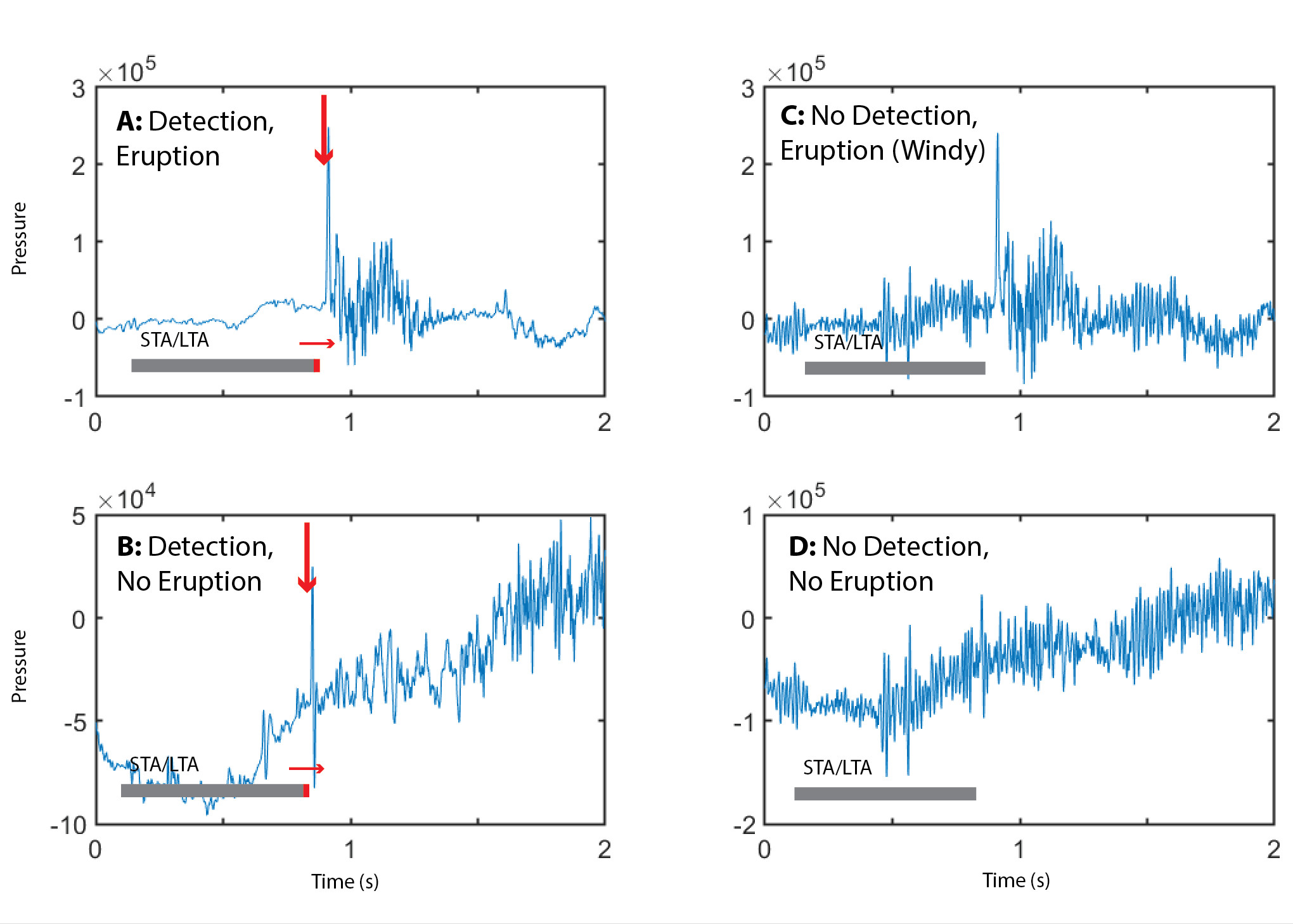
USGS: Example plots of STA/LTA alarm on infrasound knowledge for 4 attainable alarm eventualities. A reveals detection of an actual eruption, B reveals a false detection of non-volcanic change, C reveals failure to detect an actual eruption amid noisy knowledge, and D reveals no detection of any occasion of curiosity.
During eruptions, adjustments within the air strain are recorded on sound detecting sensors (like microphones), known as an infrasound or acoustic array. The determine reveals how a profitable detection of an eruption may work utilizing infrasound knowledge and the way the system might fail to detect an eruption.
The first picture (A) reveals an eruption that creates strain adjustments recorded by the sensor. The detection (marked by a crimson arrow) can be straightforward to find out utilizing an STA/LTA technique, mentioned above and proven because the gray and crimson bar on the backside of panel A. The long-term common (gray bar) is a interval earlier than the eruption and the short-term common (crimson bar) reveals when the eruption vitality is robust. In this case, the STA is far greater than the LTA and we will set the pc to ship a message when this particular situation happens.
If we subsequent think about the identical sensor which has detected one other burst (B), however this burst got here from a non-eruption supply (say a automobile, a helicopter or one other occasion away from our volcano). In this case, the volcano scientist could be alerted by an occasion that wasn’t volcanic (a false detection). Next, we present a cartoon instance the place we’ve got launched wind noise (C) into the identical eruption recorded in (A). In this case, the wind can be so sturdy that the eruption can solely simply be seen within the knowledge by the bare eye however might not be seen to the pc’s STA/LTA detector. In the ultimate instance wind noise was added to the instance which can have been a automobile or helicopter however not an eruption (D); on this case the non-eruption can solely barely be seen within the knowledge and was not detected by the STA/LTA detector.
The cartoon figures present 4 attainable outcomes that can be utilized to evaluate how good an alarming system performs. They embody: 1) detection of an actual eruption (A), 2) a false detection of non-volcanic change (B), 3) failure to detect an actual eruption (C) and, 4) not detecting any occasion of curiosity (D).
These 4 examples present how HVO scientists can assess the efficiency of our alarm programs to enhance detection of volcanic occasions and reduce the detection of noise or different exercise. The 4 examples coincide with the ideas of check circumstances for alarms utilizing the phrases: true-positive (A), false-positive (B), false-negative (C) and true-negative (D). alarm system ought to embody true-positives (volcanic occasions) and true negatives (non-volcanic occasions) and attempt to reduce false-positives and false-negatives. Too many false alerts equate to pointless lack of sleep throughout quiet intervals for a volcano. In abstract, alarm programs are an vital and evolving a part of HVO operations and are an instance of how computer systems and expertise are included in monitoring.




