SpaceX launched its enormous Super Heavy-Starship mega rocket on its seventh test flight Thursday, efficiently “catching” the primary stage booster again at its firing stand however dropping its new-generation Starship higher stage spacecraft, which apparently broke up because it was reaching area.
Telemetry from the Starship froze eight minutes and 27 seconds after launch following sudden engine shutdowns or failures. SpaceX later confirmed the ship’s destruction in a posting on X, utilizing a tongue-in-cheek description:
“Starship skilled a fast unscheduled disassembly throughout its ascent burn. Teams will proceed to evaluate knowledge from as we speak’s flight take a look at to higher perceive root trigger. With a take a look at like this, success comes from what we study, and as we speak’s flight will assist us enhance Starship’s reliability.”
SpaceX
“We (misplaced) all communications with the ship,” a SpaceX launch commentator mentioned of the Starship. “That is basically telling us we had an anomaly with the higher stage.” A second later, he confirmed: “We did lose the higher stage.”
The Federal Aviation Administration additionally reported that airline visitors at Miami International and Fort Lauderdale-Hollywood International airports was delayed as much as an hour because of what it described as a “rocket launch anomaly.”
The FAA in an announcement mentioned it “briefly slowed and diverted plane across the space the place area car particles was falling.” It mentioned regular operations had resumed.
“The FAA is conscious an anomaly occurred through the SpaceX Starship Flight 7 mission that launched from Boca Chica, Texas, on Jan. 16,” the company mentioned in a follow-up assertion, including that it’s “assessing the operation.”
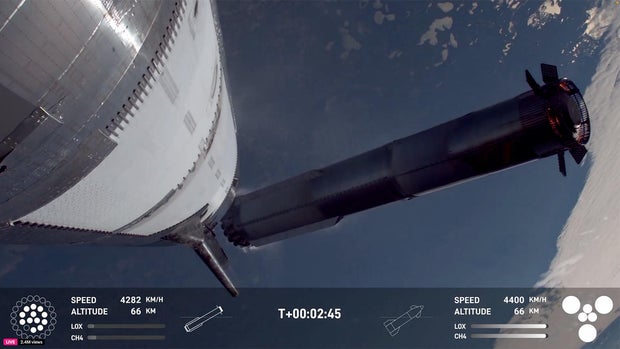
The gargantuan rocket blasted off from SpaceX’s Boca Chica, Texas, manufacturing and flight take a look at facility on the Gulf Coast at 5:37 p.m. Eastern Time, firing up 33 methane-burning Raptor engines producing as much as 16 million kilos of thrust.
Gulping 40,000 kilos of propellant per second, the booster climbed away from its launch stand and gracefully arced over to the east atop an extended jet of flaming exhaust seen for dozens of miles round.
Two minutes and 40 seconds after liftoff, the Super Heavy fell away and the Starship continued the climb to area on the ability of its six Raptor engines.
SpaceX
The booster, in the meantime, flipped round, re-ignited a number of engines to reverse course and headed again towards Boca Chica the place the distinctive mechanical arms on the rocket’s launch gantry had been open and ready.
Plummeting tail first again to Earth, the Super Heavy re-ignited its engines, tilting as they steered it to the pad, after which settled straight down between the chopsticks, which easily closed to seize their quarry in mid air.
The first such catch final October was profitable, a jaw-dropping sight to 1000’s of cheering residents and vacationers. But the Super Heavy used for the next such flight a month later was diverted to a Gulf of Mexico splashdown due to launch injury to sensors on the tower that had been wanted to assist information the descending booster into place.
New sensors with have extra sturdy shielding had been put in place to get rid of such injury and SpaceX engineers are optimistic they will quickly be recovering Super Heavy boosters with the identical regularity they’ve demonstrated with the corporate’s workhorse Falcon 9 rockets, a key aspect in SpaceX’s drive to decrease launch prices.
In protecting with the reusability theme, the Super Heavy’s 33 Raptor engines included one which flew on a earlier take a look at flight to reveal its potential to fly a number of missions.
The bulk of the upgrades examined Thursday had been constructed into what SpaceX referred to as a “new technology” Starship. Two minutes after the booster “landed,” the higher stage reached area.
SpaceX
SpaceX
But the lack of telemetry left flight controllers at nighttime about what might need occurred within the remaining phases of the ascent.
For these preliminary take a look at flights, the Starships don’t try to succeed in orbit. Instead, they loop midway across the planet and descend belly-first via a hellish blaze of atmospheric friction earlier than flipping nostril up for a tail-first, rocket-powered splashdown within the Indian Ocean.
For Thursday’s flight, main take a look at aims included restarting a Raptor engine in area and the deployment of 10 dummy Starlink mockups to check a brand new satellite tv for pc supply system that works a bit like a Pez sweet dispenser. Starships are anticipated to launch 1000’s of Starlinks after the rocket is operational.
Among the opposite upgrades had been smaller stabilizing fins, repositioned to cut back their publicity to re-entry heating, an improved propulsion avionics system, redesigned gasoline feed traces and a 25% improve in propellant quantity to enhance efficiency.
SpaceX
The redesigned avionics system features a extra highly effective flight pc, new antennas that mix alerts from Starlink and GPS navigation satellites, “good batteries” and energy models to drive two dozen high-voltage actuators and redesigned navigation sensors.
SpaceX additionally added extra cameras, with greater than 30 on board to offer direct views of important programs utilizing operational Starlink satellites to stream real-time video and knowledge to the bottom.
While the spacecraft is designed to be absolutely reusable, SpaceX has not but made any makes an attempt to seize a returning Starship or, for that matter, a Falcon 9 higher stage.
But Thursday’s take a look at flight featured a number of experiments to check quite a lot of warmth defend enhancements, together with metallic tiles and one with energetic cooling, together with dummy Starship catch fittings, to study extra about how they may reply to re-entry heating.
“This new 12 months will likely be transformational for Starship,” SpaceX mentioned on its web site, “with the purpose of bringing reuse of your entire system on-line and flying more and more formidable missions as we iterate in direction of with the ability to ship people and cargo to Earth orbit, the moon, and Mars.”
Getting the Super Heavy-Starship flying regularly is important to NASA’s Artemis moon program. NASA is paying SpaceX to develop a variant of the Starship higher stage to hold astronauts all the way down to the lunar floor within the 2027 timeframe.
To ship a Starship to the moon, SpaceX should first launch it to low-Earth orbit the place a succession of different Starship “tankers” should rendezvous, dock and autonomously refuel the moon-bound ship so it might blast out of Earth orbit and head for deep area.
Astronauts launched in an Orion capsule atop NASA’s Space Launch System rocket then will rendezvous with the Starship in orbit across the moon for the descent to the floor.
NASA’s contract requires one unpiloted lunar touchdown take a look at flight earlier than astronauts will be cleared to trip one all the way down to the floor. The ongoing take a look at program will decide when that is likely to be doable.