Sometimes science must go large. From telescopes spanning the globe to particle accelerators that may take over 24 hours to stroll round, these experiments are among the many largest ever carried out.
Gravitational wave searching
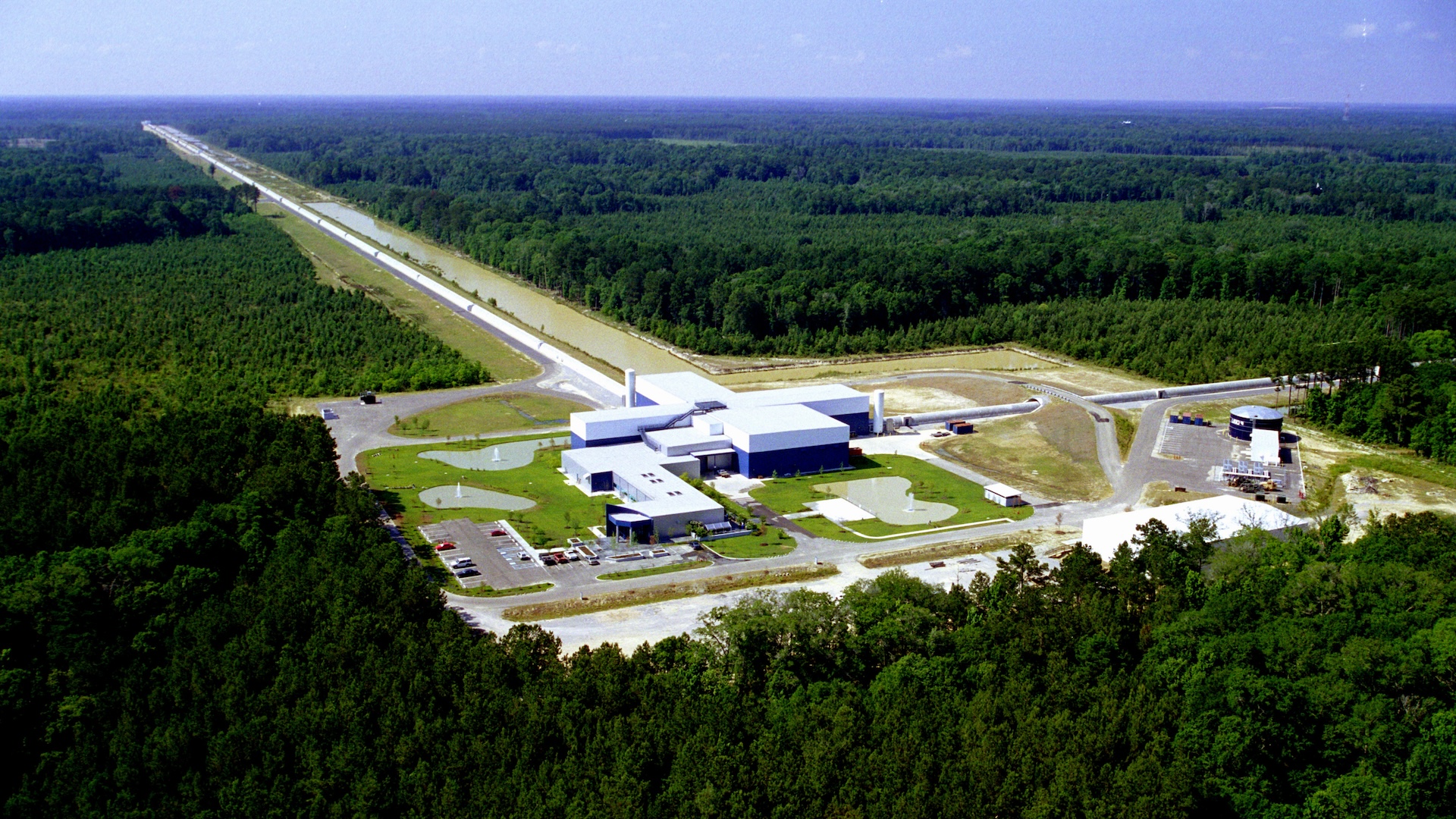
Ripples within the gravitational area of the universe,often called gravitational waves, are remnants of large galactic occasions corresponding to black gap collisions and merging neutron stars. These waves might even file echoes of the Big Bang. To detect them, scientists want large tools, such because the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO).
LIGO consists of two giant devices, every with two 2.5-mile-long (4 kilometers) arms. The devices are in Washington state and Louisiana, roughly 1,900 miles (3,000 km aside). The arms are laser interferometers, organized in L shapes. A single laser beam is break up in half, with every half despatched down one of many arms. At the top of every arm is a set of mirrors, which bounce every half laser beam round a couple of hundred instances after which again up the arms so that they reunite.
By investigating the interference sample — the best way the peaks and troughs of the sunshine waves mix — scientists can decide if a gravitational ripple occurred in the course of the experiment. If so, they’ll examine it intimately. The bigger the arms, the extra delicate the instrument, which is why LIGO boasts the longest laser interferometers ever constructed.
LIGO has detected all method of mysterious galactic phenomena, from a merger between a neutron star and (in all probability) a superlight black gap to a number of collisions between neutron stars. (It has additionally detected a flock of ravens pecking on icicles on the Washington facility — an commentary with fewer implications for the dynamics of the universe.)
Related: To hunt gravitational waves, scientists needed to create the quietest spot on Earth
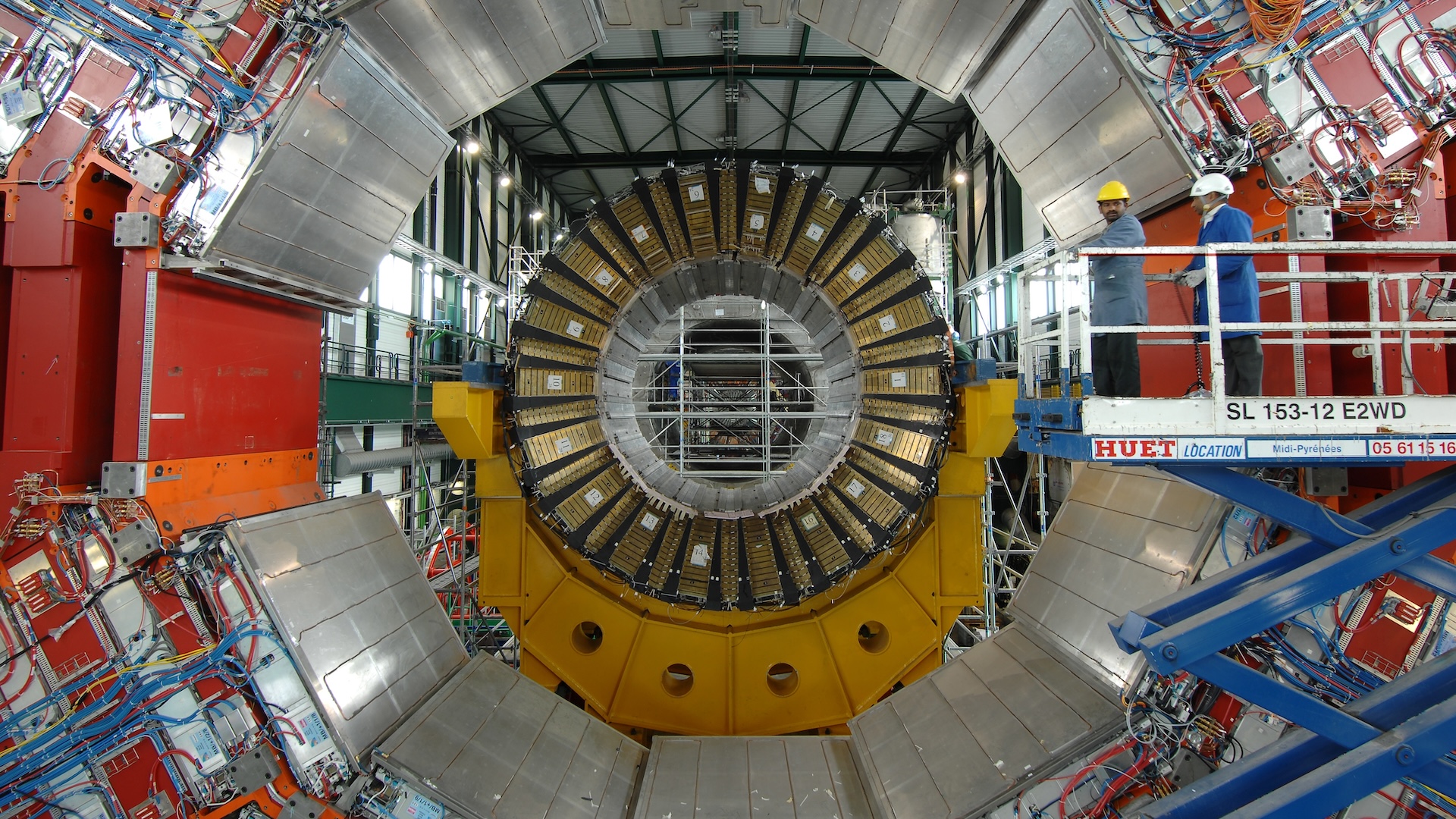
World’s largest atom smasher
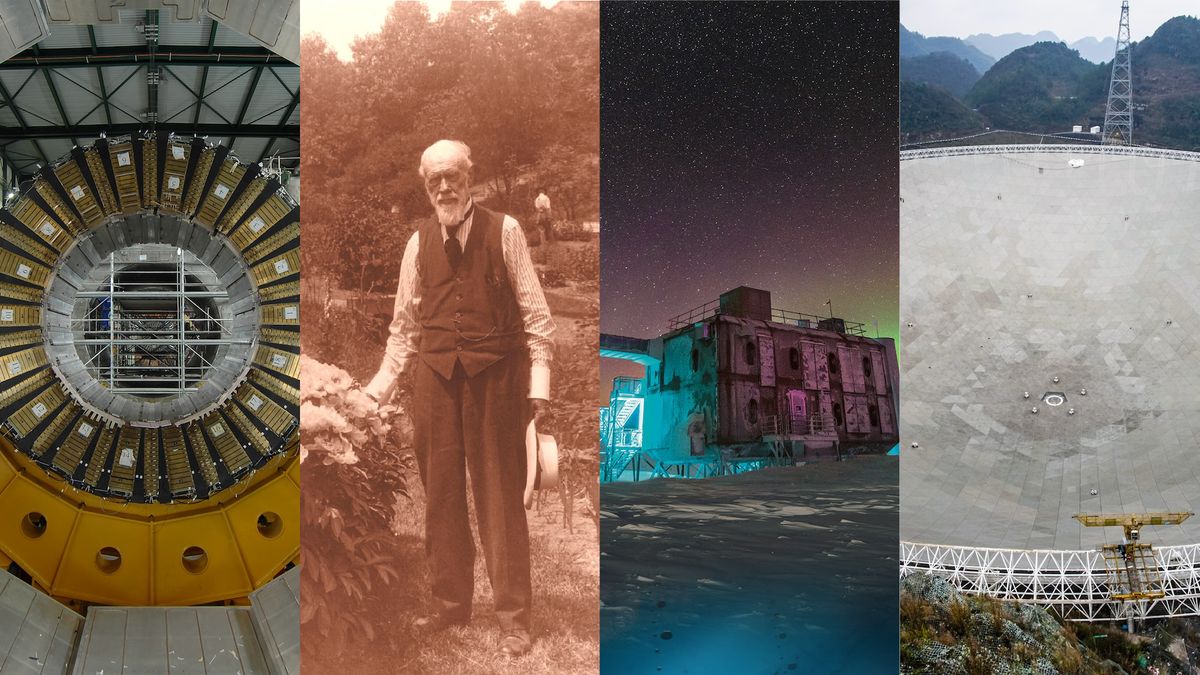
To examine the very small, scientists generally have to make use of very large devices. They do not come larger than the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the world’s largest particle accelerator. Run by CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, this 16.7-mile-diameter (27 km) ring is studded with 4 detectors, often called ATLAS, CMS, ALICE and LHCb. Befitting its location, the 7,700-ton (7,000 metric tons) ATLAS is the largest particle detector ever constructed. The instrument measures a variety of subatomic particles created when scientists zap particle beams at each other at excessive velocity, creating collisions that throw off elusive elementary particles just like the Higgs boson.
The LHC boasts over 10,000 tons (9,000 metric tons) of iron in its magnetic techniques and sufficient niobium-titanium cable to stretch to the solar and again over six instances after which between Earth and the moon one other few instances. It’s additionally the biggest, coldest fridge on Earth, as a result of the magnets have to be saved at minus 456.25 levels Fahrenheit (minus 271.25 levels Celsius), barely colder than outer house.
Miniature Amazon rainforests

Watch On
By pumping tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the environment annually by means of the burning of fossil fuels, humanity is performing an especially large-scale — and really uncontrolled — experiment. In the Amazon rainforest, researchers try to get a deal with on the implications of these greenhouse gases in a big experiment of their very own.
The mission, known as AmazonFACE, goals to amp up the carbon dioxide focus in components of the world’s largest tropical forest basin to grasp the impacts of elevated CO2 on the “lungs of the planet.”
FACE stands for “Free-Air Carbon Dioxide Enrichment.” The experiment consists of 12 observational arrays in six 98-foot-diameter (30 m) plots: three at ambient carbon dioxide concentrations and three at larger concentrations. The highest focus — 615 components per million — is predicted to be reached by the 2070s beneath a middle-of-the-road pathway to local weather mitigation wherein nations make sluggish and uneven progress towards sustainability.
Each plot comprises round 400 plant species and lots of extra specimens of fungus and soil microbes — a full ecosystem. As carbon dioxide will increase, crops photosynthesize extra shortly and launch much less water from their leaves, defined Beto Quesada, government supervisor of the mission and a researcher on the National Institute for Amazonian Research. This may assist defend the forest from the impacts of local weather change, which is predicted to convey drought to the Amazon area.
But the steadiness between these two processes and the tipping level between a wholesome forest and a collapsing ecosystem are unknown, stated David Lapola, the mission’s scientific coordinator and a researcher on the Center for Meteorological and Climatic Research Applied to Agriculture of the University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in Brazil.
“We’ll be making an attempt to resolve one of many largest uncertainties with regard to the way forward for the Amazon forest in mild of local weather change,” Lapola informed Live Science.
The researchers will measure the affect of the additional CO2 on plant physiology, together with whether or not crops in a carbon-rich environment add non permanent buildings, like leaves, or extra everlasting options, corresponding to wooden. This is vital to review as a result of wooden locks up carbon for hundreds of years, whereas carbon used to develop leaves reenters the setting inside a yr or two. The experiment is predicted to run for a minimum of a decade.
“It is an ecosystem-scale experiment,” Quesada stated, “but it surely’s far more than that. It goes to the social, economical and environmental impacts that the lack of the rainforest can have.”
A very large carbon seize facility
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change , humanity would not simply must cease releasing carbon dioxide into the environment to keep away from elevating the worldwide temperature greater than 1.5 C (2.7 F) above preindustrial ranges. We even have to tug carbon again out of the air.
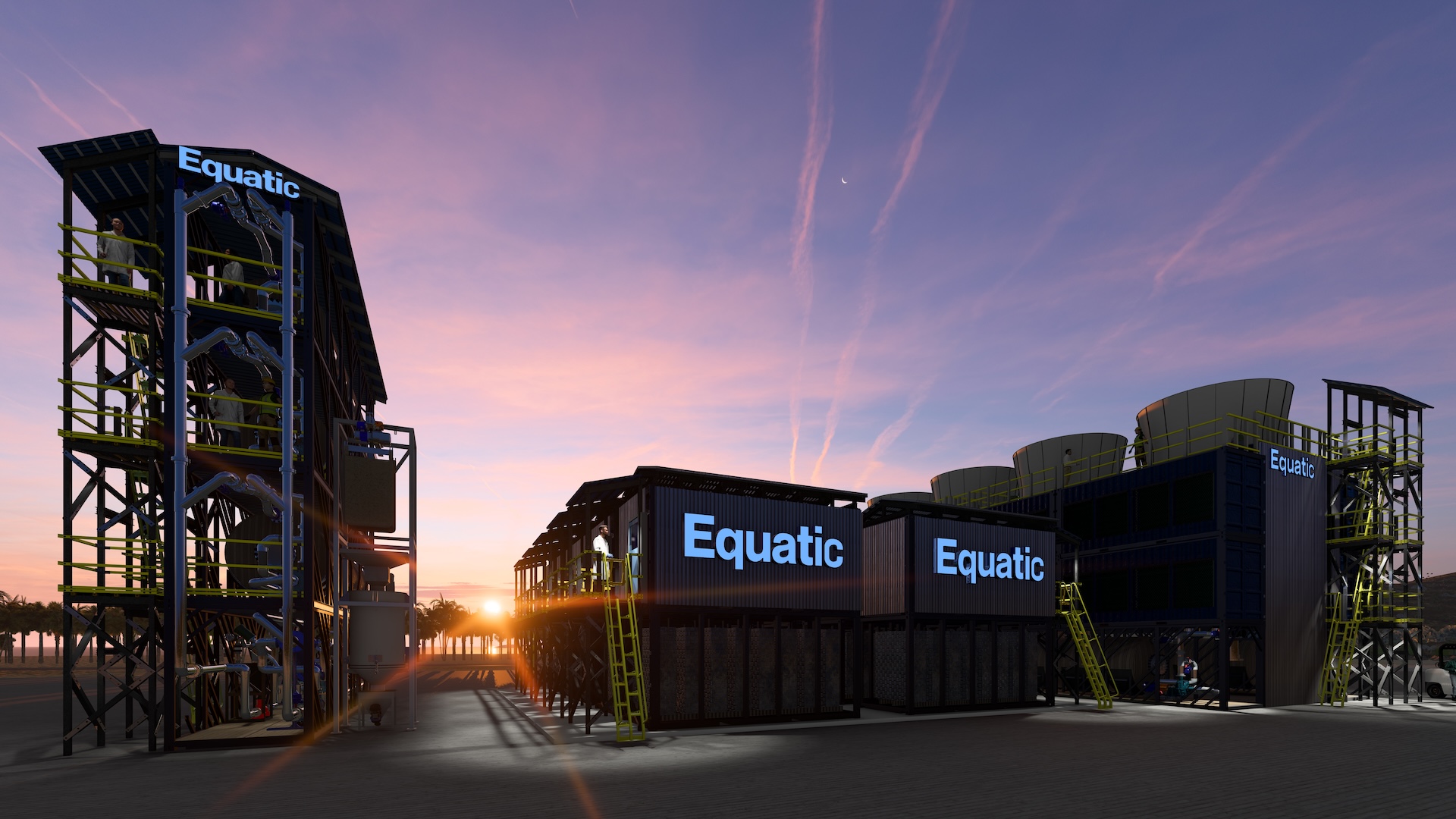
By 2050, 6 to 10 gigatons of carbon equal have to be eliminated to keep away from hitting the warming threshold set by the Paris Agreement. There are many choices for carbon sequestration, corresponding to capturing industrial waste streams and burying biomass. But the first-ever commercial-scale marine carbon-capture facility is aiming to take away carbon proper from the ocean.
The ocean naturally takes up carbon from the environment, however it may well’t soak up it quick sufficient to make a climatic distinction on the size of a human life span. The carbon-capture firm Equatic is aiming to speed up that timeline.
“Equatic’s business plant takes 5 minutes to take away one tonne of carbon by pumping seawater in, operating {an electrical} present by means of, after which contacting the seawater with a stream of air from the environment,” Edward Sanders, Equatic’s chief working officer, informed Live Science in an e mail. “An equal space of open ocean takes 12 months to take away that one tonne of carbon.”
The chemical course of that removes the carbon from the seawater additionally creates hydrogen, a chemical that is for a lot of industries and might be burned as gas to energy 40% of the power prices of the carbon-capture course of. The carbon is then sequestered as bicarbonate, the identical materials present in seashells, which is able to preserve the carbon out of the environment for as much as 10,000 years. This bicarbonate might be put again within the sea or be utilized in fertilizers. It can even function a constructing materials in coastal restoration, Sanders stated.
Similar experiments have been finished on a pilot scale, however Equatic’s facility in Quebec will intention to sequester 120,700 tons (109,500 metric tons) of carbon per yr beginning in 2027. It would be the first commercial-scale try to make a dent within the greenhouse fuel overload within the environment through the oceans.
A world of infants
How do infants be taught language? When do they perceive gestures? Are they hardwired to mimic adults? All of those questions are powerful to reply, as a result of infants are difficult analysis topics, liable to crying and sudden naps.
The issue of recruiting busy, exhausted dad and mom and their often-uncooperative infants to do analysis research led to the start of ManyBabies. This international collaboration of researchers from over 50 nations swimming pools smaller-scale research of toddler improvement into giant pattern sizes — typically 1000’s of infants.
The analysis collaboration has discovered that infants actually do favor child discuss to adult-style speech, suggesting that the pure tendency to coo a few child’s toesie-woesies is an evolutionary adaptation that helps them be taught language. Researchers are actually learning how infants develop an understanding of different individuals’s beliefs — a ability often called concept of thoughts — and making an attempt to determine once they be taught to use summary guidelines to conditions. They’re additionally creating new strategies, corresponding to eye-tracking know-how and noninvasive mind imaging strategies, to search out out what infants are studying.
A city-size chunk of Antarctic ice
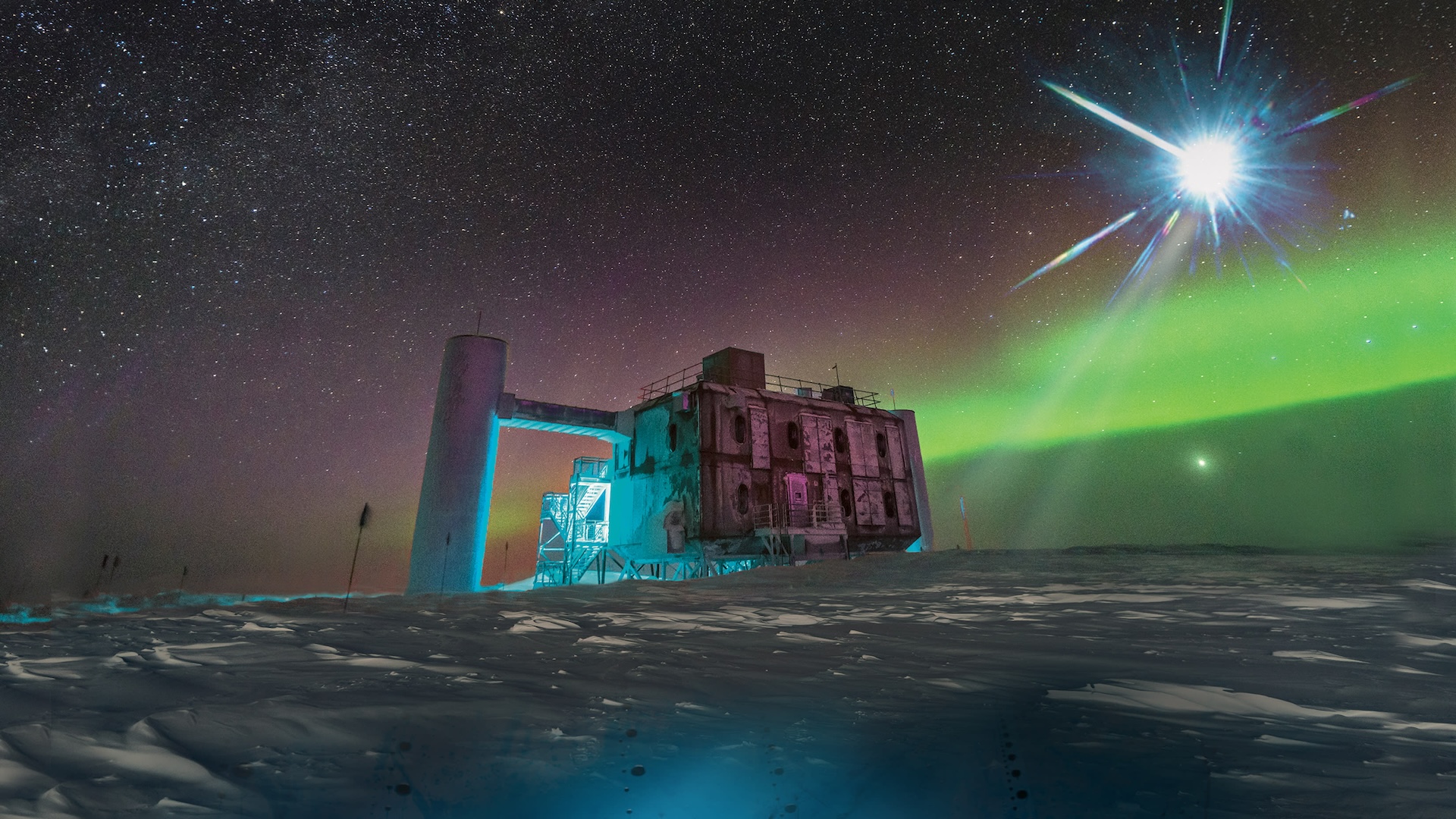
Neutrinos are sometimes known as “ghost particles” as a result of the almost massless particles barely work together as they cross by means of matter. Because they hardly ever perturb different matter, they’re troublesome to detect. But discovering neutrinos from distant cosmic sources is usually a method to observe and analyze high-energy environments corresponding to pulsars, supernovas and black holes.
“We want a really large goal, corresponding to a billion tons of fabric, to have a preventing probability to — from time to time — catch a few of them,” stated Albrecht Karle, a professor of physics on the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Those billions of tons of fabric come from a cubic kilome ter of ice on the South Pole. Karle is the affiliate director of science and instrumentation on the IceCube Neutrino Observatory, which is outstanding in each its measurement and remoteness. IceCube consists of a sequence of optical detectors on strings, operating by means of holes drilled 4,800 to eight,000 toes (1,450 to 2,450 meters) into the Antarctic ice.
When a neutrino interacts with the ice, it creates different particles that emit tiny flashes of sunshine. The sensors detect this mild and might measure its wavelength to disclose the flavour of neutrino and its supply. (That’s why a clear medium, corresponding to ice, is vital, Karle informed Live Science — the fabric must be clear for the sunshine to be detectable.)
IceCube information has allowed scientists to make the primary map of the Milky Way utilizing matter, not simply mild. The observatory has additionally revealed unusual, high-energy cosmic rays with no simple rationalization. And Karle and his colleagues have plans to go even larger. They’re presently drafting a plan for IceCube Gen-2, which might broaden the present observatory to eight instances its present measurement, with a 200-square-mile (500 sq. kilometers) radio detector array to amplify incoming neutrinos. This would massively enhance the sensitivity of the detector and permit higher classification of the neutrinos that cross by means of it, Karle stated.
A globe-spanning psychology examine
The COVID-19 pandemic was its personal international experiment, albeit one with an enormous variety of uncontrolled variables. Psychologists took benefit of this shared international expertise with a few of the largest psych research of all time.
One, with nearly 50,000 individuals, discovered that individuals with a stronger nationwide identification responded extra cooperatively with public well being efforts. Across 67 nations, individuals with a stronger feeling of identification with their nation had been extra probably than these with a weaker sense to remain put throughout quarantine, to help public well being insurance policies, and to say they engaged in social distancing and stricter bodily hygiene after the onset of the pandemic. National identification is a few sense of collective belonging and mutual cooperation, the authors famous. This is completely different from beliefs about nationwide superiority, which is a perception that one’s nation is healthier than others.
“These outcomes are in keeping with the social psychological literature on the advantages of figuring out with one’s social teams,” the authors wrote. “They additionally underscore a possible good thing about [national identity], which is perhaps salient throughout a nationwide or international well being disaster.”
Another main COVID-era examine, with almost 27,000 individuals, discovered that messages emphasizing autonomy inspired adherence to social distancing suggestions. The examine examined completely different social distancing messaging methods throughout 89 nations and located that people who centered on private autonomy and the worth of considerate decisions had been simpler than messages that emphasised disgrace and stress.
A centuries-long plant experiment
Small in measurement however large in period, Michigan State University botanist William James Beal’s seed viability experiment has been operating constantly since 1879. The objective of this experiment is to learn how lengthy seeds of various crops can lie dormant earlier than sprouting. To discover out, Beal buried bottles of seeds from 23 completely different crops 3 toes
(0.9 m) deep in an undisturbed (and secret) location so they might not sprout. He began unearthing bottles in five-year increments — a niche that was ultimately stretched to each 10 years.
Incredibly, the experiment continues to be operating — and now, researchers are stretching the hole between bottle openings to twenty years, as a result of seeds simply preserve sprouting. The final bottles had been opened in 2021, and the following set will get their time to shine in 2040. The findings have implications for plant evolution and seed germination and is perhaps helpful for understanding the method of habitat restoration and seed banking, or saving seeds for potential use within the distant future.
The plan is to maintain the experiment operating till 2100, in line with Michigan State. Will that be sufficient time to search out the utmost age any of their seeds can sit earlier than sprouting? Probably not; crops have sprouted from seeds as much as 2,000 years previous.
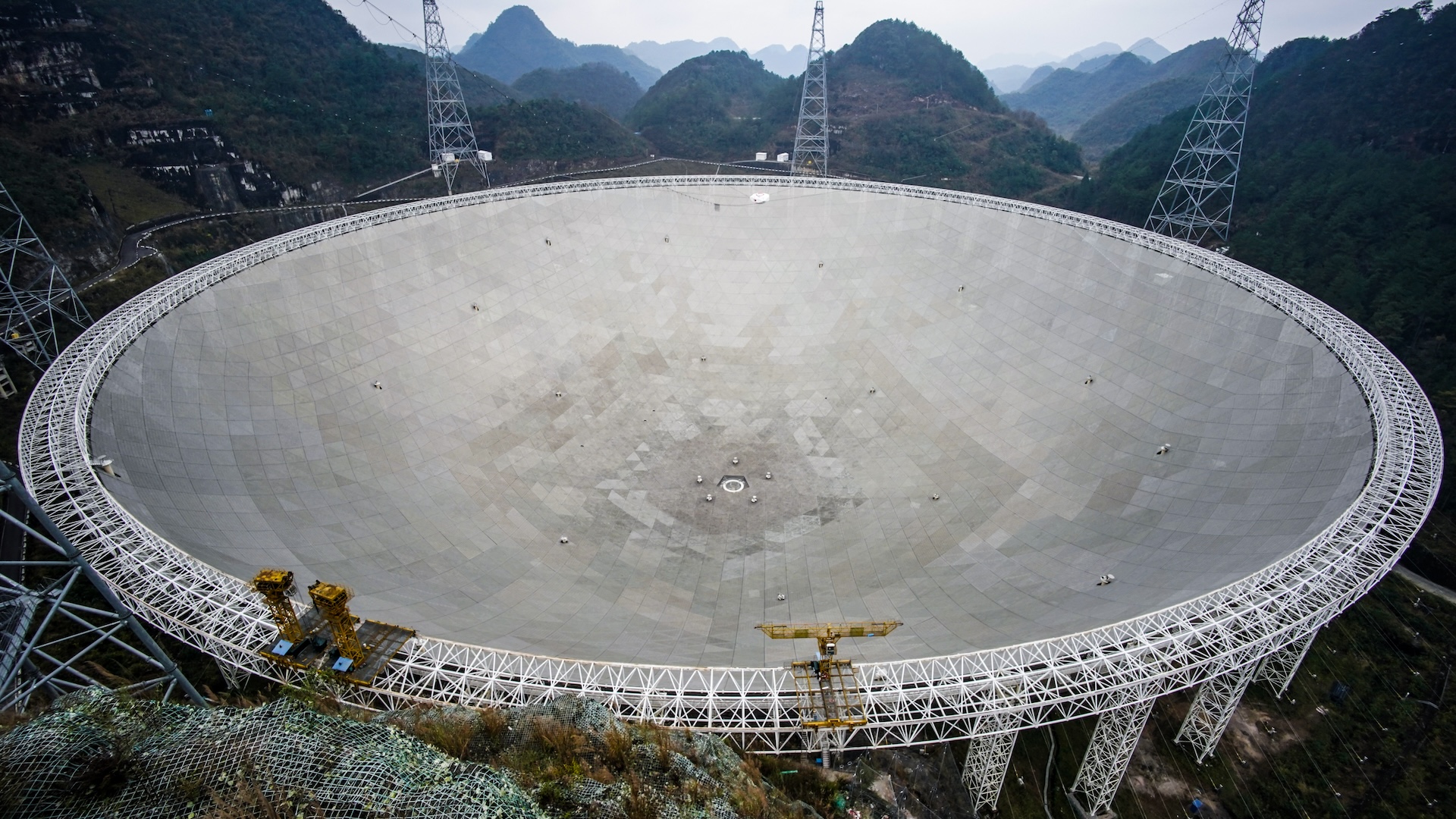
China’s monstrously enormous radio telescope
China’s Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) array is the world’s largest single-dish radio telescope, at 1,640 toes in diameter. Holding up the dish are 328-foot (100 m) metal towers and 6,670 cables. Now, a brand new section of building is including 24 131-foot (40 m) movable radio telescopes to the power.
The array sits in a pure melancholy known as Dawodang within the rugged topography of China’s Guizhou province. This shields it from electromagnetic interference from human sources and will increase its sensitivity to cosmic radio indicators. The objective, in line with the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), is to make use of the telescope’s sensitivity to conduct large-scale surveys of the universe.
FAST began working at full capability in 2020 and has already found greater than 200 pulsars, that are rotating neutron stars that emit common pulses of electromagnetic radiation. These embody the pulsar PSR J0318+0253, which, at 4,000 light-years away and with a rotation interval of lower than 10 milliseconds, is without doubt one of the faintest radio millisecond pulsars ever discovered, in line with CAS.
A telescope community that spans many of the world
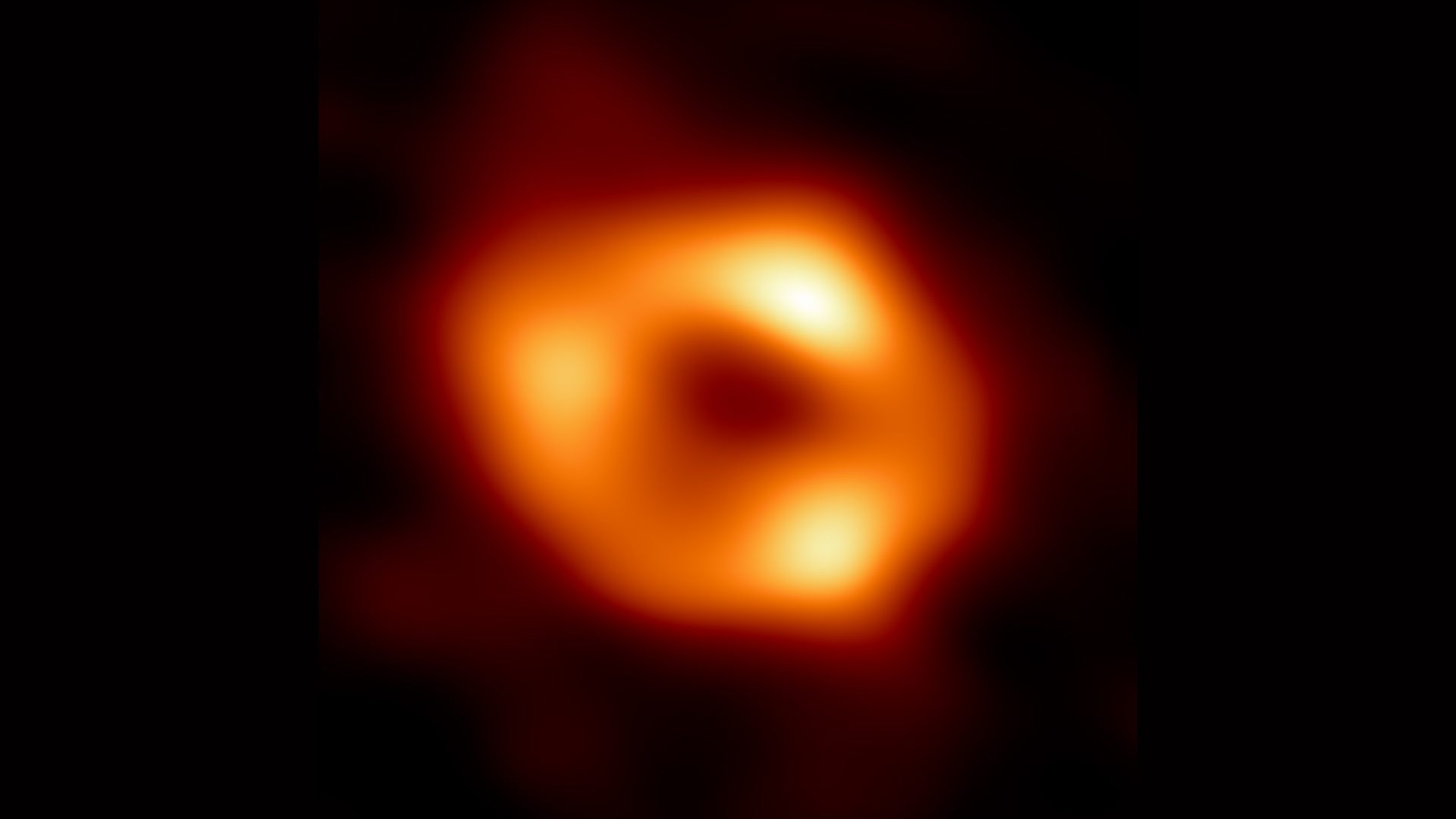
What may you see with a telescope the dimensions of the world? Well, the black gap on the coronary heart of the Milky Way, for one factor.
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a community of radio telescopes stretching from Greenland to the South Pole (north to south) and from Spain to Hawaii (east to west). The precise variety of observatories within the EHT shifts with time (it was 11 as of 2021), and new telescopes can be added sooner or later — together with one deliberate for the Canary Islands.
These observatories work collectively to detect faint radio indicators related to black holes. This collaboration generated the first-ever view of a black gap, together with the contours of the occasion horizon, the boundary by means of which no mild or matter can escape. Scientists have additionally seen the mesmerizing swirl of the black gap on the heart of our personal galaxy and noticed big electromagnetic jets taking pictures from the supermassive black gap on the coronary heart of the galaxy Perseus A. Recently, they peered into the center of a quasar, a superluminous galactic core powered by an enormous black gap.
The EHT must be giant as a result of it depends on the flexibility to watch the universe constantly over eight- to 14-hour stretches from a number of angles, in line with the Black Hole Partnerships for International Research and Education, a collaboration that develops the algorithms utilized by the telescope. These algorithms additionally depend on Earth’s rotation to overlap observations, permitting researchers to mix photographs from quite a few telescopes. Only then can they peer into a few of the largest, but hardest-to-see phenomena within the universe.