Mark Zuckerberg set the internet abuzz this week when the Meta CEO introduced that the tech large would not conduct unbiased fact-checking. The program, carried out in 2016, shall be changed with Meta’s personal model of Community Notes, a crowdsourced strategy to reviewing on-line content material employed by X, the social media platform beforehand generally known as Twitter.
So what precisely is Community Notes, and the way does it work?
How Community Notes works
Meta hasn’t launched specifics about the way it will empower customers of Facebook, Instagram and different social platforms to watch content material, mentioned Melissa Mahtani, government producer at CBS News Confirmed.
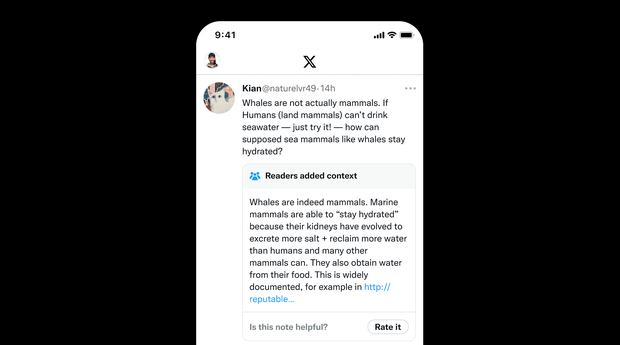
On X, Community Notes works by leaving fact-checking as much as the group. Approved contributors name out content material deemed false or deceptive by attaching notes offering extra context. Here’s an instance of a group notice offered by X on its website:
X
Becoming an accredited contributor on X “would not take a lot,” Mahtani mentioned. Any X person with an lively telephone quantity and who’s been on the platform for at the very least six months with no violations is certified to volunteer to be a contributor, she mentioned. Contributors are protected by anonymity.
When a publish is deemed false or deceptive by an accredited contributor, the particular person will publish a notice that gives customers with further context. The notice seems beneath the unique publish.
Once a notice is added by an accredited contributor, it’s nonetheless not seen to common customers on X. Before that occurs, different accredited contributors should vote on whether or not the notice is useful. This is the place “issues get difficult” mentioned Mahtani.
Is the notice useful?
Once a notice is added to a publish on X, different accredited contributors price it on its utility.
Explained Mahtani, “Other contributors want to check out the sourcing, the accuracy of that notice, and vote on whether or not or not it is useful. If they vote that it is useful — that is the difficult half — the corporate says that an algorithm takes a have a look at the ideological spectrum of all these contributors who voted. If they deem that these voters are numerous, it will get revealed.”
The algorithm decides
According to X’s web site, the aim of its so-called bridging-based algorithm is to “determine notes which are useful to a broad viewers throughout views.”
In different phrases, if the algorithm finds that contributors who voted on a given notice characterize an ideologically numerous group, then the notice turns into seen on the platform. But if the algorithm finds that the voting contributors are too uniform of their political beliefs — a doable signal of bias — “the general public by no means sees it,” Mahtani mentioned.
Problems with X’s system of crowd-based fact-checking come up when a sound notice calling out misinformation is not rated as useful by a various sufficient group of contributors to fulfill the algorithm, and is due to this fact by no means seen by readers. The velocity at which a notice is made public can be necessary, in order that false or deceptive data is not given the chance to unfold unchallenged.
A report in October by the nonprofit Center for Countering Digital Hate analyzed the Community Notes function and located that correct notes correcting false and deceptive claims in regards to the U.S. elections weren’t displayed on 209 out of a pattern of 283 posts deemed deceptive — or 74%.
More data on how X’s Community Notes works will be discovered on X’s Community Notes page.
CBS News has a devoted editorial workforce, CBS News Confirmed, that fact-checks claims, exposes misinformation and offers vital context. You can observe CBS News Confirmed on Instagram and TikTok.